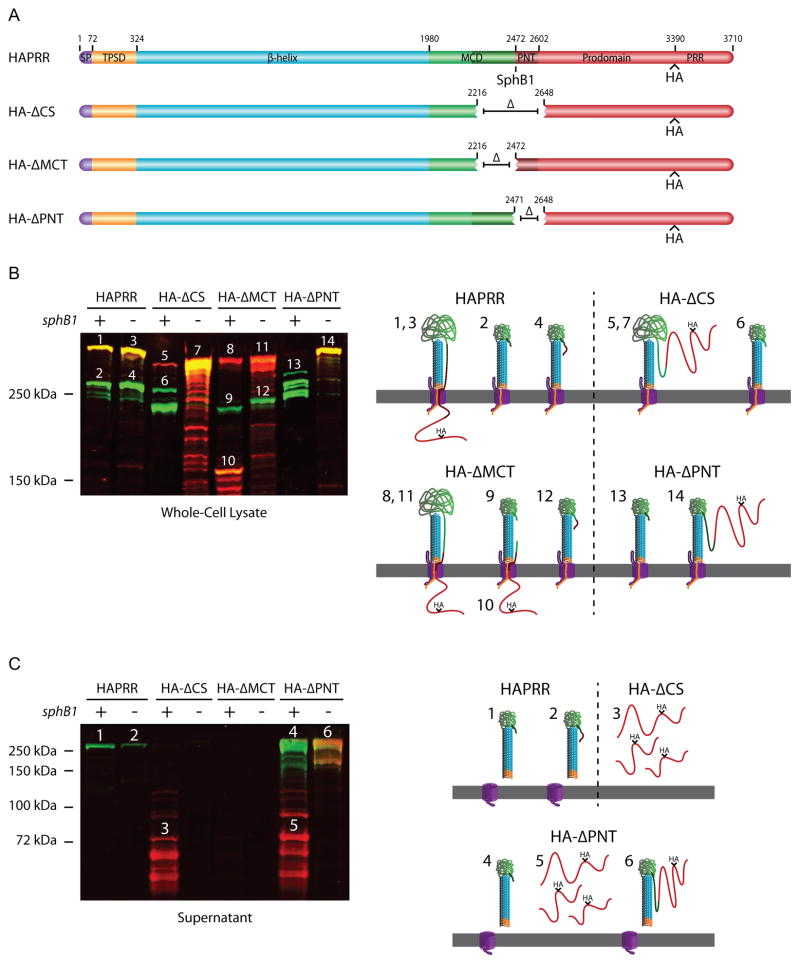
Figure 6.
The MCT controls FHA release and the PNT keeps the prodomain C-terminus intracellular. (A) Schematic of FhaB proteins used in experiment. The MCT is represented as dark green. (B) Anti-MCD and anti-HA immunoblot of whole-cell lysates. Numbers above protein bands correspond to illustrations on the right side of the figure. Illustrations 1–4 represent products of the HAPRR strain, 5–7 represent products of the HA-ΔCS strain, 8–12 represent products of the HA-ΔMCT strain, and 13 and 14 represent products of the HA-ΔPNT strain. Layout of these illustrations is as described in Figure 4B. (C) Anti-MCD and anti-HA immunoblot of concentrated supernatants. Numbers above protein bands correspond to illustrations on the right side of the figure. Illustrations 1 and 2 represent products of the HAPRR strain, 3 represents the product of the HA-ΔCS strain, and 4–6 represent products of the HA-ΔPNT strain. Layout of these illustrations is as described in Figure 4B. Deletion of the MCT prevents FHA release, while deletion of the PNT promotes release. Additionally, deletion of the PNT results in translocation of the prodomain into the extracellular space where it can be separated from FHA in an SphB1-dependent manner.