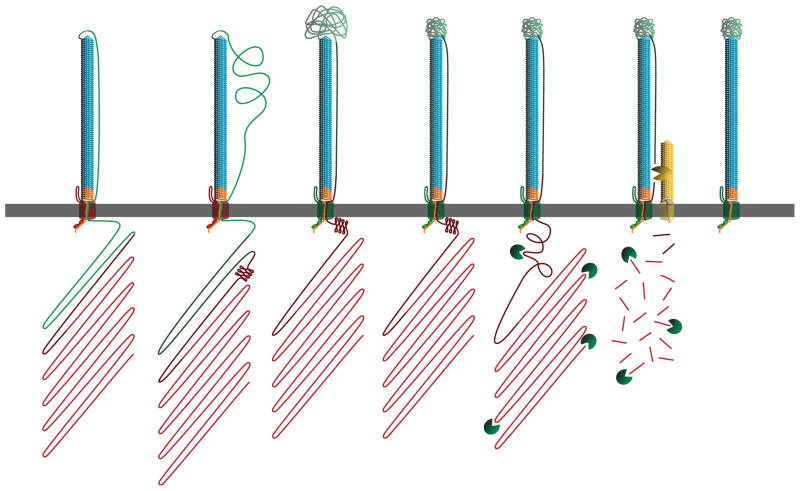
Figure 8.
Revised model for FHA biogenesis. Our model continues from Supplemental Figure 1A, with the β-helix surface-localized and the MCD and prodomain still inside the cell. During the secretion process, the PNT adopts a conformation that prevents prodomain transit through FhaC. Next, the MCT of FhaB translocates to the extracellular space, priming FhaC for release of FHA, as indicated by the shift in FhaC color from red to green. The translocation-impaired PNT confers tension across the extracellular space to the MCD, restricting the conformations the MCD may sample while folding. FhaB undergoes maturation into FHA upon completion of MCD folding, with FHA maturation being accomplished by SphB1-independent cleavage, degradation of the prodomain and SphB1-dependent cleavage. At this point, FHA is fully mature and can remain either surface-associated or be released into the supernatant.