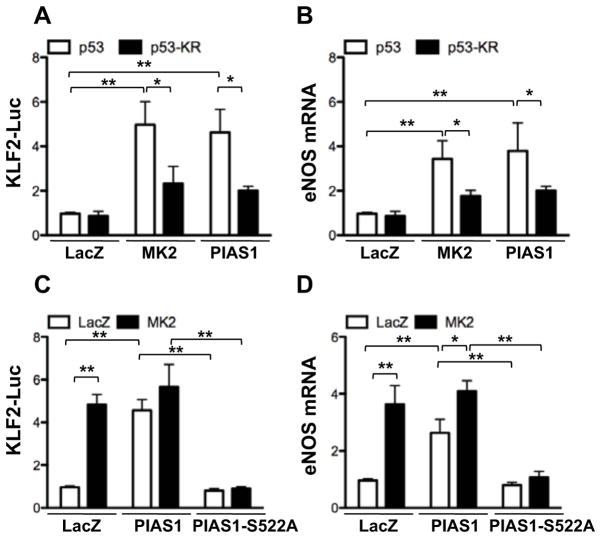
Figure 3. MK2-mediated PIAS1 phosphorylation regulates p53-SUMOylation and subsequently enhances KLF2 promoter activity and eNOS mRNA expression.
(A, B) Effects of p53 SUMOylation on KLF2 promoter activity (A) and eNOS mRNA expression (B) in HUVECs transduced with Ad-LacZ, Ad-MK2, or Ad-PIAS1 were evaluated using dual-luciferase reporter assays (A) and real-time quantitative PCR (B). HUVECs were transduced with Ad-LacZ, -MK2, -PIAS1, or -p53-KR for 18 hrs and further transfected with the KLF2 promoter activity reporter construct for 18 hrs, then assayed for firefly and Renilla luciferase activities (A). After 18 hrs of the adenovirus transduction, HUVECs were assayed for eNOS mRNA levels (B). (C) HUVECs were transduced with Ad-LacZ, -PIAS1-WT, -PIAS1-S522A, or -MK2 for 18 hrs, and KLF2 promoter activity (C) or eNOS mRNA levels (D) were detected as described for A–B. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (n=3 mice; mean ± S.D.). (E) A signaling scheme describing the relationship between the inhibitory effect of p53 on KLF2-eNOS expression and MK2-induced PIAS1-S522 phosphorylation which leads to p53 SUMOylation.