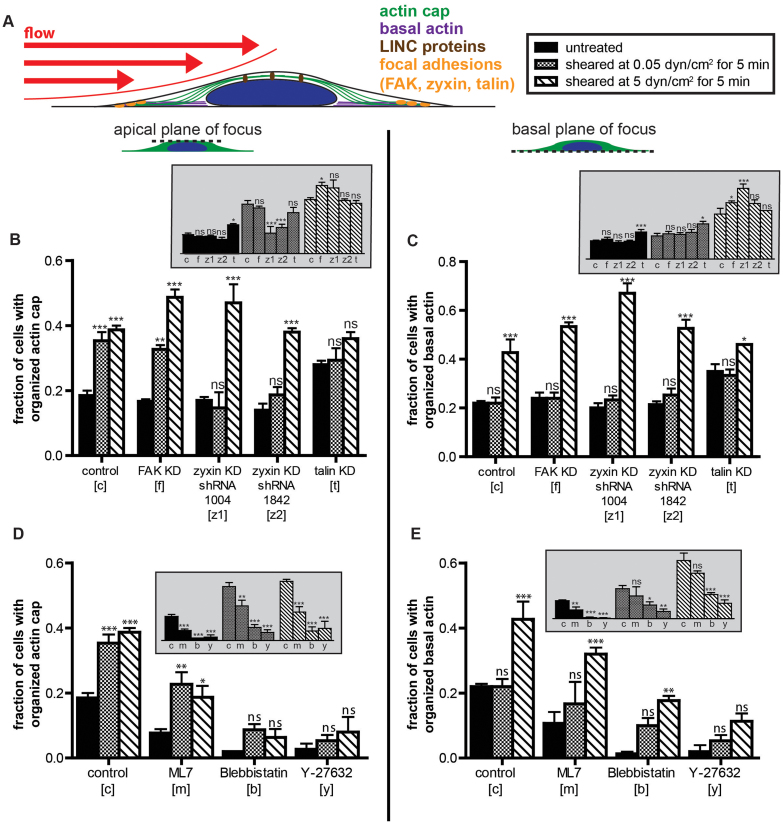
Figure 4. Shear-induced actin cap formation is mediated by zyxin at low shear stress and talin at high shear stress.
(A). Schematic of an adherent cell subjected to a shear flow of controlled flow rate applied for a controlled duration. Focal adhesion proteins (shown in orange) and LINC complex proteins (shown in brown, see Fig. 5) were knocked down or knocked out and the resulting cells were exposed to shear flow. Status of the actin filament network at the apical surface of the nucleus and the basal surface of the cells is examined by epifluorescence microscopy. (B) and (C). Percentages of control and focal adhesion knockdown MEFs featuring an organized actin cap (B) and organized basal stress fibers (C) in cells with the absence/presence of shear flow of shear stresses of 0.05 dyn/cm2 and 5 dyn/cm2 applied for 5 min. Cells were separately shRNA-depleted of focal adhesion proteins FAK, zyxin, or talin. (D) and (E). Percentages of control and actomyosin contractility drug-treated MEFs featuring an organized actin cap (D) and organized basal stress fibers (E) in cells with the absence/presence of shear flow of shear stresses of 0.05 dyn/cm2 and 5 dyn/cm2 applied for 5 min. Cells were treated with the drugs ML-7 to inhibit myosin light chain kinase, blebbistatin to inhibit myosin II, and Y-27632 to inhibit Rho-kinase. For all main panel graphs, significances compare unsheared cells (black bars) to sheared cells (patterned bars) using two-way ANOVA tests. Inset graphs show the same bars but compare differences among different knockdown strains/drug treatments subjected to the same shear stress. For all data shown, ***, **,*, and ns indicate p value <0.001, <0.01, <0.05, and >0.05, respectively. α = 0.05 was used for all significance tests. Three independent experiments were conducted to quantify a total of 150 cells per condition.