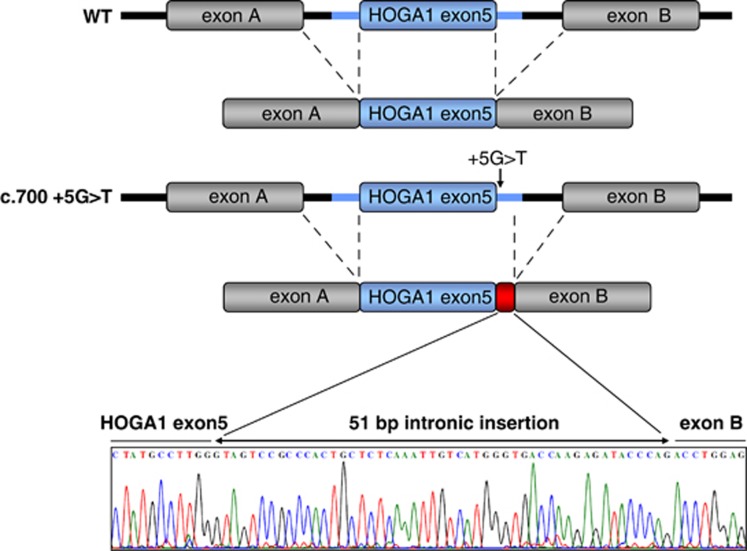
Figure 2.
pSPL3 splicing assay and sequencing result for the frequent splice-site mutation c.700+5G>T compared with wild-type cDNA. Fragments of the human HOGA1 gene containing exon 5 were cloned into the splicing vector pSPL3 generating plasmids pSPL3-HOGA1-Exon5-WT and pSPL3-HOGA1-Exon5+5G>T. After transfection mRNA was extracted from cells and reverse transcribed cDNA was amplified using specific primers within flanking pSPL3 exons. The G>T sequence alteration on position +5 cripples the wild-type donor site and activates an aberrant donor site on position +52, which leads to the in-frame insertion of 51 nucleotides of intron 5 (17 amino acids) into the native protein. The interrupted black lines mark the spliced out intronic sequences. The blue box indicates HOGA1 exon 5 while the blue lines represent the flanking 500 bp of upstream and 900 bp downstream intronic sequence of HOGA1 exon 5. The gray boxes mark pSPL3 exons A and B with the adjacent black lines depicting the flanking intronic sequence of the pSPL3 exons. The red box represents the 51 bp insertion resulting from the c.700+5G>T splice-site mutation.