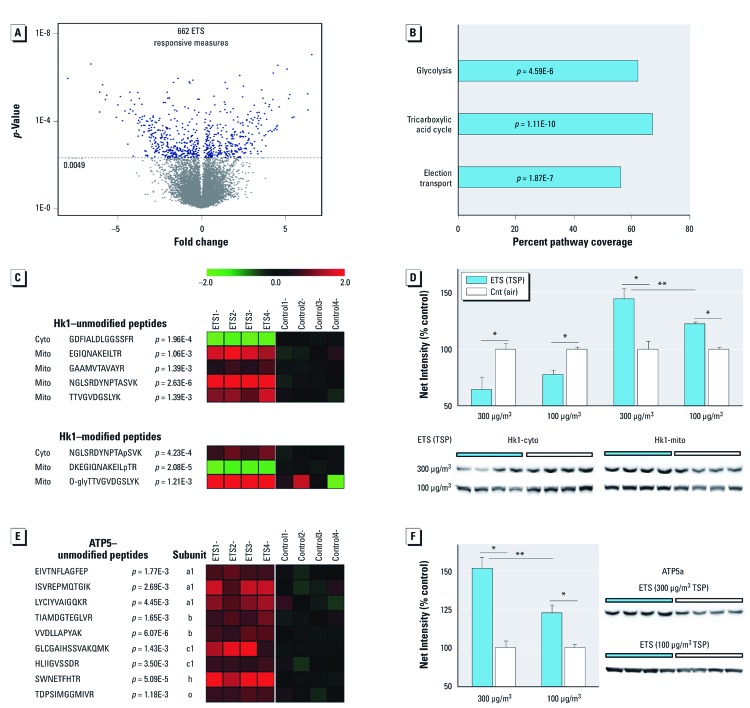
Figure 2.
Significant cerebellar proteome perturbation after ETS exposure with dose-dependent up-regulation of aerobic processes. Animals were exposed daily to ETS or plain air (Cnt). (A) Quantitative proteomics revealed 662 ETS300-exposure responsive peptides in the cerebellar cortex, denoting significant change among 389 proteins; data are presented as fold change (n = 4/group; corrected α = 0.0049). (B) Aerobic respiration pathways prominently altered in the ETS-responsive neuroproteome; data are presented as percent pathway coverage (corrected α = 0.016). (C,E) Heatmap plots of ETS300-responsive peptide measures for Hk1 (C; unmodified and posttranslationally modified) and ATP5 (E) (log2, ratio to control; n = 4/group; p-values reported). (D,F) Dose-dependent immunoblot protein measures of Hk1 (D) and ATP5a (F); cytosolic (cyto) and mitochondrial (mito) protein levels graphed for Hk1 to assess subcellular translocation; data are presented as mean ± SE; n = 4/group. *p < 0.05 compared with controls. **p < 0.01 compared across dose.