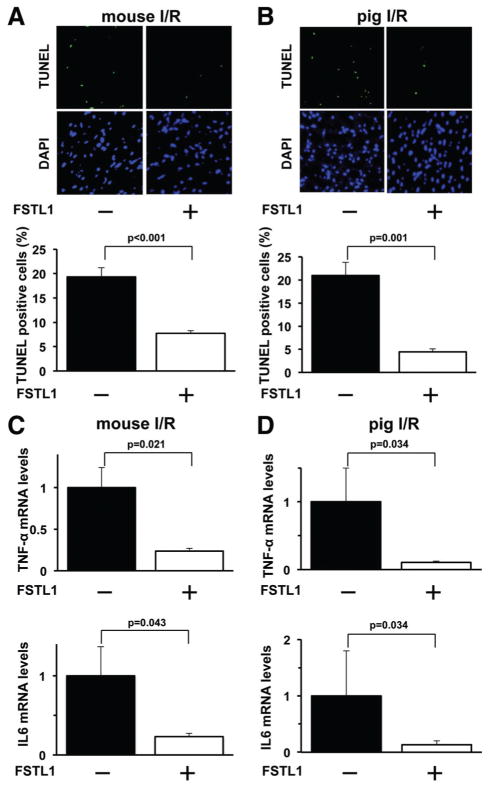
Figure 2.
Administration of follistatin-like 1 (FSTL1) protein attenuates apoptosis and inflammatory responses in the ischemic myocardium of mice and pigs. A, Systemic delivery of FSTL1 attenuates apoptosis in the ischemic heart of mice. Upper panels show representative photographs of mouse heart sections stained with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL; green) and DAPI (blue). Lower graph shows quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive nuclei (n=5). B, Intracoronary administration of FSTL1 to pigs inhibits apoptosis in the ischemic myocardium. Upper panels show representative pictures of heart sections stained with TUNEL (green) and DAPI (blue). Lower graph shows quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive nuclei (n=4). C and D, Delivery of human FSTL1 suppresses expression of proinflammatory cytokines in the ischemic hearts of mice (C) and pigs (D). The mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) was measured by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction method and expressed relative to β-actin levels (n=5). I/R indicates ischemia/reperfusion.