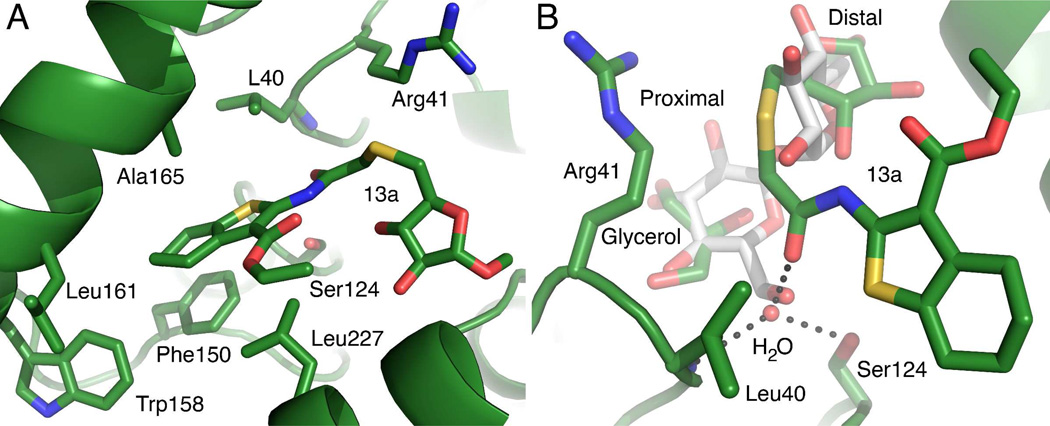
Figure 6.
Interactions between 13a and the Ag85C active site. Two views of the Ag85C active site are shown from different orientations A) Non-specific interactions. The Ag85C protein backbone is shown as the green ribbon. The carbon atoms are in green, nitrogen atoms are in blue, oxygen in red and sulfur in yellow. The location of the serine nucleophile is shown as a reference. All of the hydrophobic residues within 4 Å of the thiophene moiety are shown as well as the R41 side chain that interacts with the thioether linker. B) The superposition of the trehalose-bound Ag85B and the 13a-bound Ag85C structures shows overlap of the trehalose and 13a binding sites. The trehalose from the Ag85B structure is shown with gray carbon atoms. All other atom types are colored as in panel A. The distal glucosyl moiety of trehalose and the methylarabinoside of 13a are clearly occupying the same region within the active site. The proximal glucosyl and an ordered glycerol molecule also superimpose well and form similar hydrogen bonding interactions with Ag85. The ordered water molecule near O6 of the Ag85b-bound trehalose is shown. The dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds between this water molecule and the 13a amide carbonyl, the side chain of Ser124, and the backbone amide of Leu40, which forms part of the oxyanion hole. The length of these hydrogen bonds range from 2.6 to 3.0 Å.