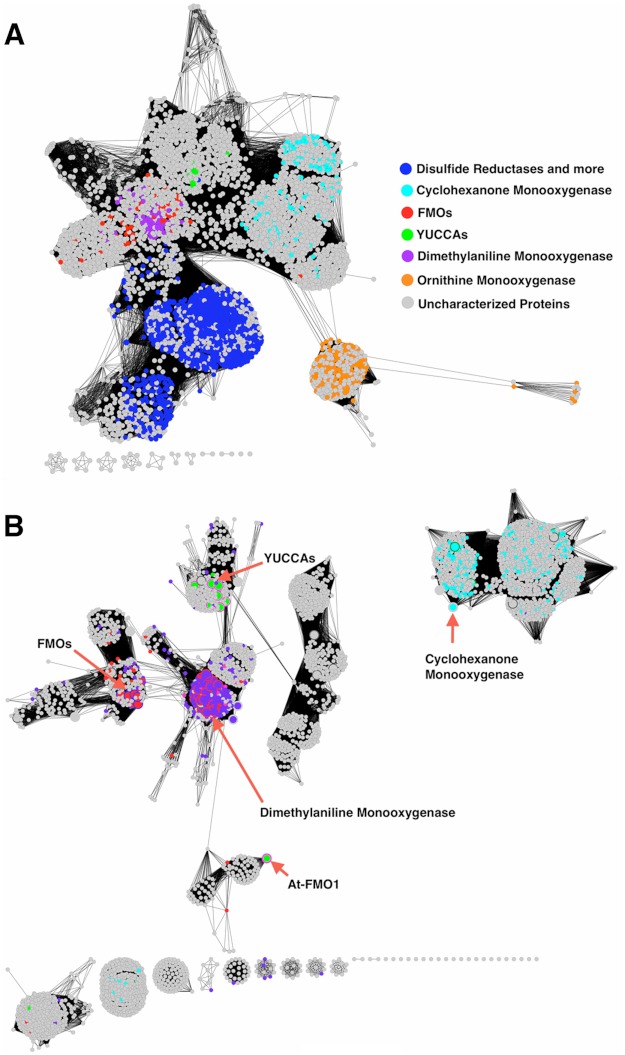
FIGURE 6.
Sequence similarity networks showing relationships of YUCs to their homologs. The names of protein classes are as shown in the legend and colored as annotated in the Uniprot database. Nodes in gray color are proteins with unknown or un-annotated functions. The 11 YUCCA proteins from Arabidopsis form a cluster at the center of the network. Cyclohexanone monooxygenases are representative BVMOs. Dimethylaniline monooxygenase is encoded by the mammalian liver fmo3 gene. Ornithine monooxygenase is a representative siderophore-associated N-monooxygenase. The islands at the bottom of each panel represent small, isolated clusters of distantly related sequences. A, the network was generated with a low stringency E-value cutoff at 1e−10. At this level of stringency, YUCs are connected to several flavoprotein families including reductases. A total of 4306 sequences with <70% pairwise sequence identity are shown. B, the network generated at a significantly more stringent E-value cutoff of 1e−45 (4188 sequences) includes the sequences shown in the red brackets from A. As the stringency was incrementally raised from 1e−10, the ornithine monooxygenase cluster separated first from the network (less closely related to the YUCs), followed by the reductase cluster (more closely related). The lack of connections between the YUCs and cyclohexanone monooxygenases indicates that they are more distantly related than the YUCs and liver FMOs. The large nodes with red borders in this figure are experimentally characterized proteins.