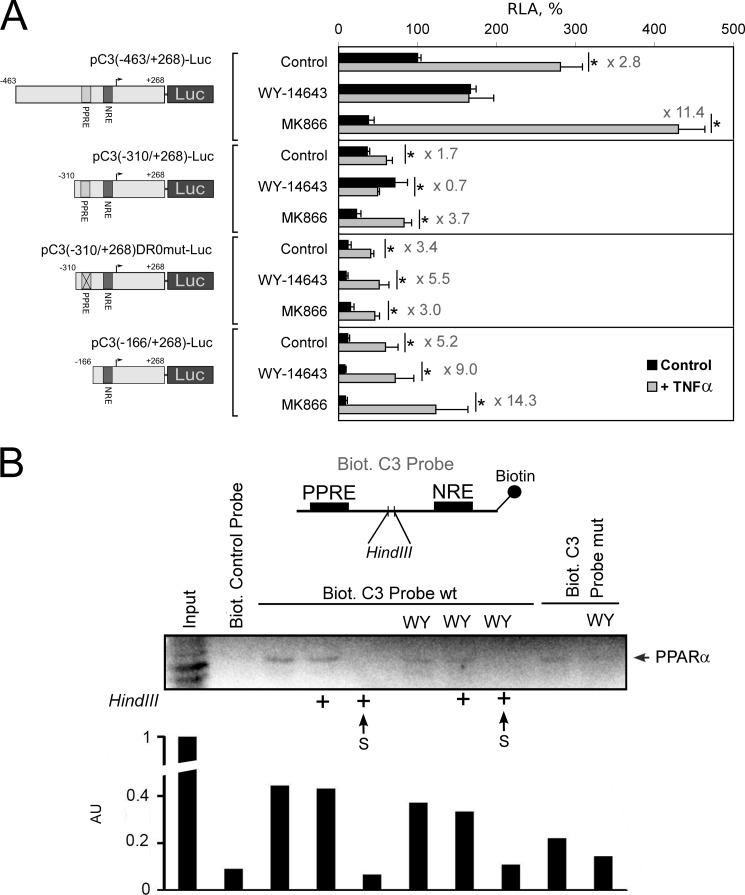
FIGURE 6.
PPRE within the human C3 promoter is important for the PPARα-mediated inhibition of the TNFα-induced activation of C3 gene transcription. A, luciferase assay. HepG2 cells were transfected by the plasmids containing fragment of the human C3 promoter with (pC3(−463/+268)-Luc and pC3(−310/+268)-Luc) or without (pC3(−310/+268)DR0mut-Luc and pC3(-166/+268)-Luc) PPRE and treated with WY-14643 (10 μm) or MK886 (10 μm) and/or TNFα (50 ng/ml) for 24 h. RLA, relative luciferase activity (100% in control HepG2 cells transfected with pC3(-463/+268)-Luc). Levels of TNFα-mediated activation of the human C3 promoter activity are shown. Black bars correspond to TNFα-untreated cells; gray bars correspond to TNFα-treated cells. Values are presented as means ± S.E. (error bars) of four independent experiments. The statistical analyses of differences between compared groups (control or treated HepG2 cells) were performed using an unpaired Student's t test (*, p < 0.05). B, DNA affinity precipitation assay from HepG2 cell nuclear extracts using biotin 5′-end-labeled fragment of human C3 promoter that contains the PPRE (Biot. C3 Probe wt) or mutated PPRE (Biot. C3 Probe mut) and NRE separated with HindIII restriction site. HepG2 cells were treated with TNFα and treated or not with WY-14643 (WY, 10 μm) for 24 h. After nuclear protein binding, probes were precipitated with anti-biotin beads, cross-linked by formaldehyde, and digested or not with HindIII (marked by + in the case of treatment with HindIII) (see “Experimental Procedures” for details). Proteins from precipitates and supernatants (S) were analyzed by Western blot using antibody against human PPARα. Biot. control probe, biotin-labeled site B from human apolipoprotein A-I hepatic enhancer (binds with HNF3β; negative control). Arbitrary units (AU) determined by densitometry of PPARα bands are shown.