FIGURE 7.
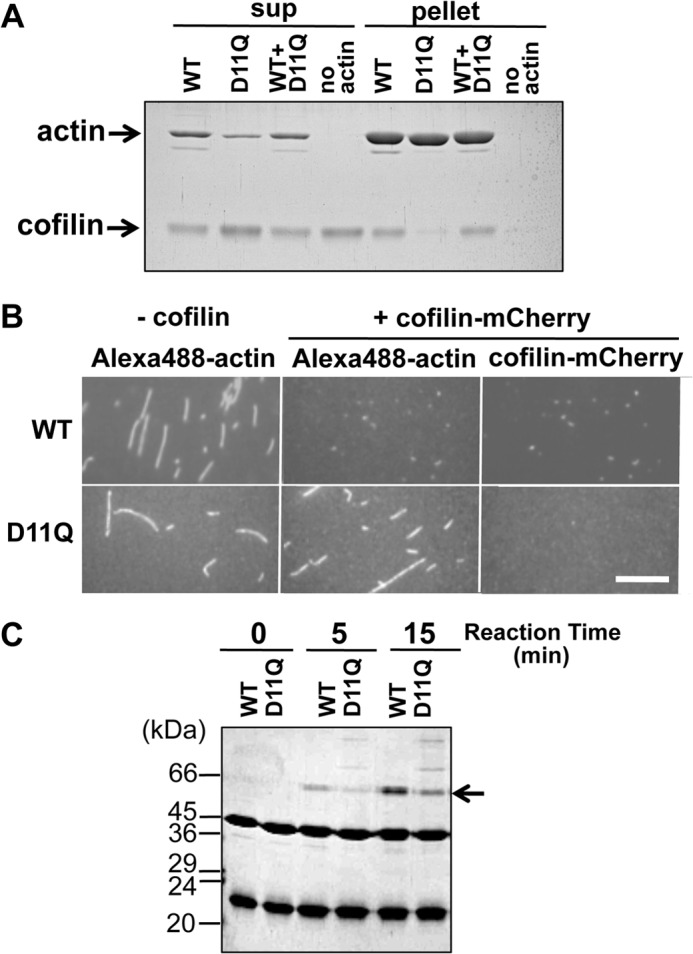
Cofilin binding. A, cosedimentation of 5 μm WT, D11Q, and 1:1 mixture polymers with 2.5 μm cofilin at pH 6.5. Supernatant (sup) and pellet fractions after ultracentrifugation were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Densitometric analyses of three sets of data showed that 49.5 ± 4.7, 0.57 ± 0.09, and 42.8 ± 2.1% of cofilin cosedimented with WT, D11Q, and WT+D11Q filaments, respectively. B, fluorescence microscopic observation of binding of cofilin-mCherry to WT or D11Q actin filaments labeled with Alexa-Fluor 488. Bar, 15 μm. C, cofilin binding to monomeric actin. Binding of 14 μm cofilin to 7 μm monomeric WT or D11Q actin in G-buffer, detected by cross-linking with 40 mm 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide for 5 min, followed by SDS-PAGE. Arrow shows the position of the cross-linked actin-cofilin. Average of three independent measurements indicated that the cross-linking of D11Q actin was 47 ± 15% slower than WT actin, and this difference is statistically significant with p < 0.05 by Student's t test. Higher molecular weight ladders formed in D11Q-cofilin cross-link reactions were formed even when D11N or D11Q actin, but not WT actin, was treated with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide in G-buffer in the absence of cofilin.
