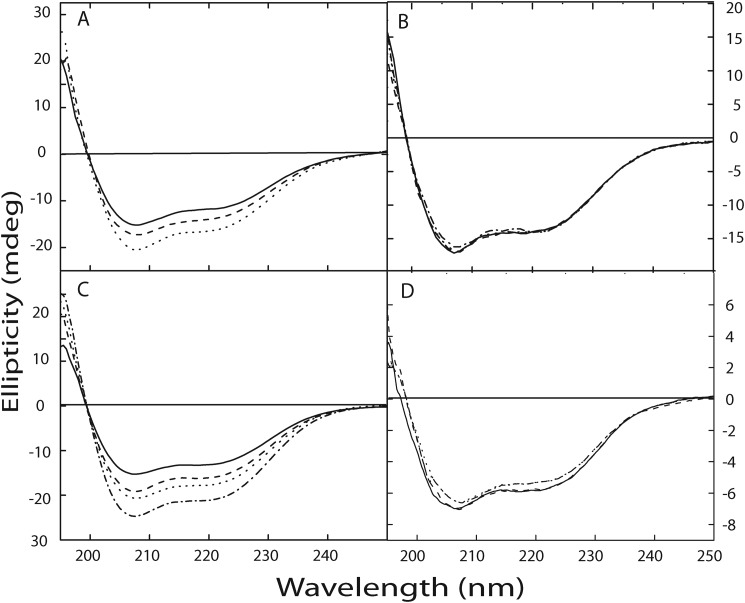
FIGURE 6.
Zn2+ induced changes in secondary structure of calnuc. Changes in the secondary structure of the protein upon interaction with Zn2+ were determined using far-UV CD spectra. The far-UV CD spectrum of calnuc and its mutants, illustrating a largely α-helical structure, were recorded in 20 mm Tris buffer containing 50 mm NaCl, pH 7.5. Spectra are representative of independent experiments repeated several times at 25 °C. Panel A, changes in the secondary structure of apocalnuc full-length upon Zn2+ binding are shown. The solid line denotes the spectra corresponding to apocalnuc only (0.4 μm), and the dashed and dotted lines represent the changes upon the addition of 10 and 20 μm Zn2+, respectively. Panel B illustrates that mutation at the Zn2+-binding site does not exhibit any changes in the secondary structure upon Zn2+ addition. The solid line denotes the spectra corresponding to the apo form of the Zn2+-binding site mutant (0.4 μm), and dashed and dotted lines represent the presence of 10 μm and 20 μm Zn2+, respectively. Panel C, changes in the secondary structure of the apocalnuc N fragment upon Zn2+ binding. The solid line denotes the spectra corresponding to apocalnuc N fragment (0.8 μm), and the dashed, dotted, and dash-dot-dashed lines represent the changes upon the addition of 10, 15, and 20 μm Zn2+, respectively. Panel D shows changes in the secondary structure of apocalnuc C fragment upon titration with Zn2+. The solid line denotes the spectra corresponding to apocalnuc C fragment (0.6 μm), and the dashed, dotted, and dash-dot-dashed lines represent the changes upon the addition of 10, 15, and 20 μm Zn2+, respectively.