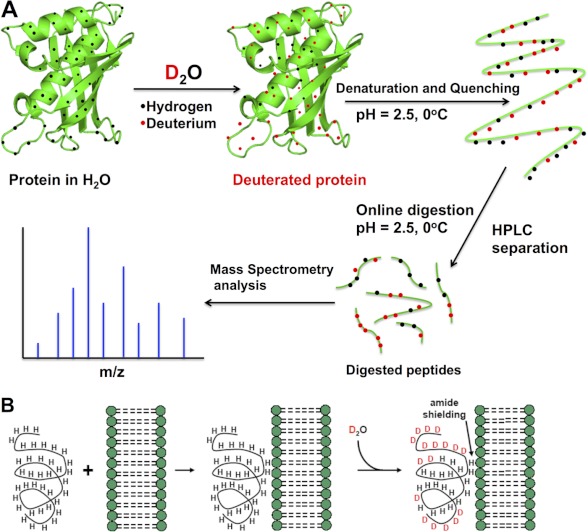
FIGURE 1.
Basis of H/D exchange. A, the protein of interest is incubated with deuterated water and labeled via exchangeable hydrogens. The exchange is then quenched to lock the deuterium atoms in position by lowering the pH of the protein-containing solution (which also denatures the protein) and lowering the solution temperature. The protein is then loaded onto an HPLC column that contains an immobilized protease that digests the protein into peptide segments. The reversed-phase column also separates these peptide segments according to their hydrophobicity. The HPLC eluent is directly connected to the mass spectrometer, where the mass analysis is carried out (the peptide segments may be further fragmented in the mass spectrometer for analysis). B, PLA2/lipid membrane interactions by DXMS. The peptide region of a protein associated with a membrane is less prone to H/D exchange (amide shielding), and this information can be used to infer this peptide region's interaction with a lipid membrane.