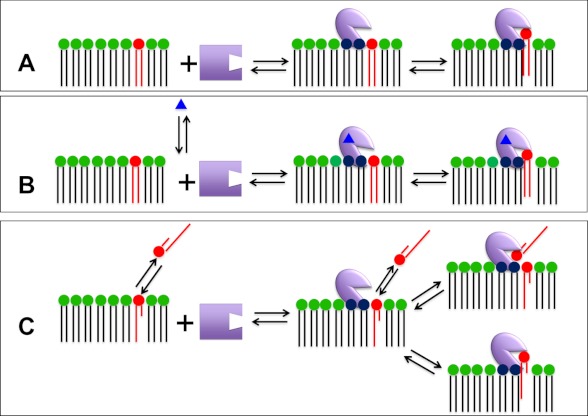
FIGURE 2.
Possible binding modes for PLA2 via its membrane interaction site, another allosteric site, and its catalytic site. A, the enzyme associates with the membrane interface via its membrane interaction site, which is distinct from its catalytic site. Once associated with the membrane, a phospholipid substrate molecule is bound by the catalytic site. B, regulated enzymes bind traditional small molecule activators or regulators, referred to as “allosteric ligands” (blue triangles), which are bound to an allosteric site on the enzyme to facilitate optimal interfacial binding via the membrane interaction site. C, for PLA2s that act on water-soluble monomeric (or small aggregated) substrates, the enzyme associated with the interface through the membrane interaction site may, in principle, access a substrate phospholipid residing in either the aqueous or membrane phase.