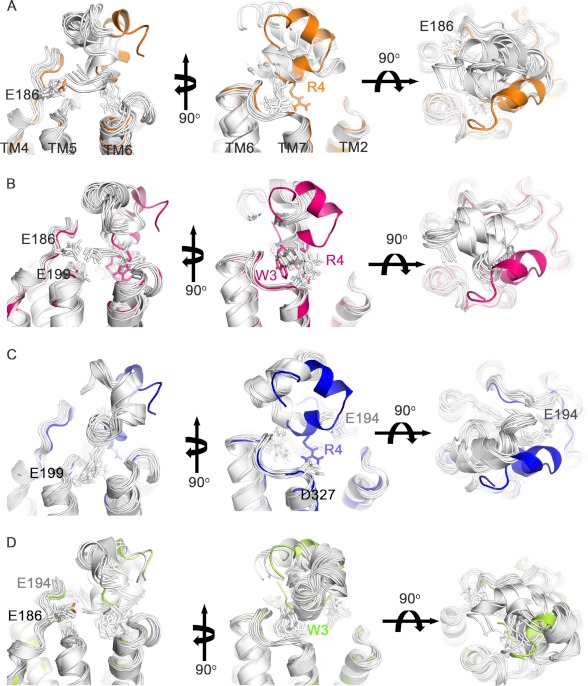
FIGURE 8.
Docking of ρ-TIA analogs and ρ-TIA to the α1B-AR and mutants. The 10 lowest energy docking complexes for each simulation are shown. All panels are prepared in the same orientation for ease of comparison, with water molecules not shown for clarity. A, docking of W3A-ρ-TIA to α1B-AR showed ∼25° rotation along the y axis (left and right) and/or z axis (middle), compared with that of ρ-TIA in α1B-AR. An additional salt bridge is observed between the positively charged N termini of W3A-ρ-TIA and Glu-186 of α1B-AR. B, docking complexes of ρ-TIA to α1B-AR-S318A/F330A showed a similar orientation to that of W3A-ρ-TIA to α1B-AR. A potential salt bridge is predicted between the positively charged N termini of W3A-ρ-TIA and Glu-186 or Glu-199 of α1B-AR. C, docking complexes of W3A-ρ-TIA and α1B-AR-S318A/F330A showed a different binding mode (∼180° rotation along the y axis) to that of ρ-TIA in α1B-AR, with Arg-4 of ρ-TIA-W3A forming a salt bridge with either Glu-199 or Glu-194, instead of Asp-327. D, R4A-ρ-TIA to α1B-AR showed rotation angles of ∼20° and ∼50° along the y and/or z axis, respectively, with the N terminus forming a salt bridge with either Glu-186 or Glu-194 on α1B-AR.