FIGURE 2.
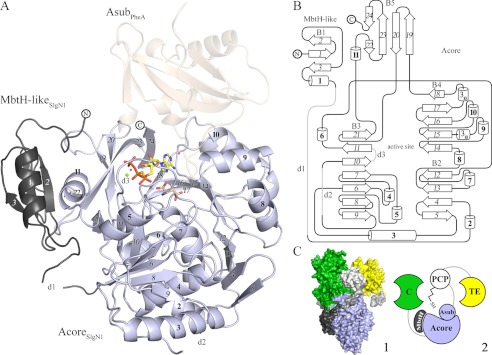
A, overall structure of SlgN1. The MbtH-like domain (dark gray) of SlgN1 interacts with helix α11 of the Acore domain (blue-white). AMPcPP (yellow), a modeled magnesium ion (green), and two structurally conserved water molecules are bound in the active center of SlgN1ΔAsub-AMPcPP. Secondary structural elements are labeled as in the topology plot (B). The amino acid substrate 3-methylaspartate (wheat) was modeled into the active center of SlgN1ΔAsub-AMPcPP. Superposition of PheA shows no interaction of the Asub domain (wheat, transparent) with the MbtH-like protein. B, topology plot of SlgN1. The structure is folded into two domains (MbtH-like domain and Acore domain) and contains five β-sheets (B1–5), consisting of 24 strands (italic), 11 α-helices (bold), two 310-helices, three disordered regions (d1–3), and several loop regions. The plot is not drawn to scale. C, model of the position of an MbtH-like protein within a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (1). Surfactin A synthetase C (SrfA-C, PDB code 2VSQ) with its four domains as follows: adenylation (light blue), condensation (green), PCP (white), and thioesterase (TE) (yellow). Linkers are depicted in light gray. The MbtH-like domain of SlgN1 (dark gray) is represented in complex with SrfA by a superposition of the A domains. This figure shows that the expected interface region between the adenylation domain and the MbtH-like domain is not blocked by other domains of the surfactin A synthetase (2). Schematic representation of one.
