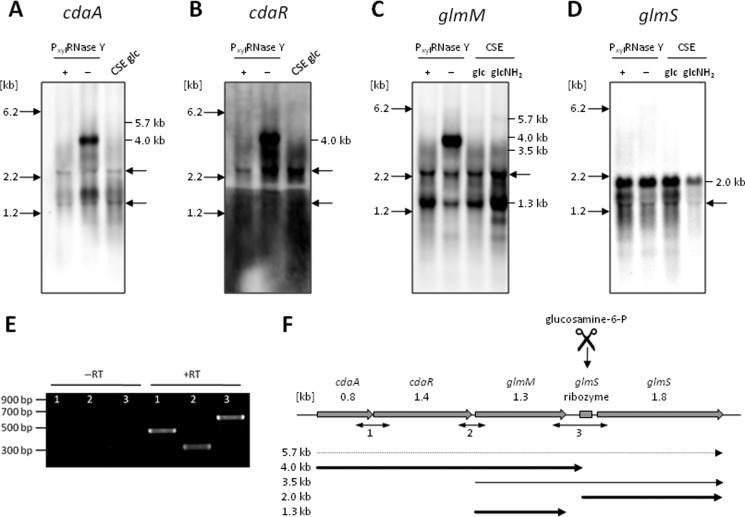
FIGURE 1.
Genetic organization of the cda-glm operon. A–D, Northern blot analysis of the cda-glm gene cluster using riboprobes specific for cdaA (A), cdaR (B), glmM (C), and glmS (D). RNA was isolated from B. subtilis 168 grown in CSE minimal medium supplemented with glucose (0.5%) (glc) or glucosamine (0.5%) (glcNH2). For the depletion of the essential RNase Y, B. subtilis GP193 was grown in CSE supplemented with glucose and with (+) or without (−) xylose (2.0%). 5 μg of total RNA was separated by electrophoresis in 1.0% agarose gels, and after blotting, nylon membranes were hybridized to gene-specific riboprobes as indicated. Note that the probes cross-hybridized with the 16 and 23 S rRNAs. The sizes of 16 S rRNA and 23 S rRNA are indicated by arrows. Moreover, the exposure time for glmS (D) was reduced compared with the other blots, and thus, the 3.5-kb transcript was not detected. E, RT-PCR analysis. Total RNA was used as a template in the reverse transcription reaction with a random nonamer primer. Regular PCRs were carried out subsequently for the amplification of different parts of the mRNA transcript using primer pairs indicated in F. As a negative control, RNA template without addition of reverse transcriptase was used (−RT). Experiments were carried out with two biological replicate samples at least three times each. F, summary of the genetic and transcriptional organization.