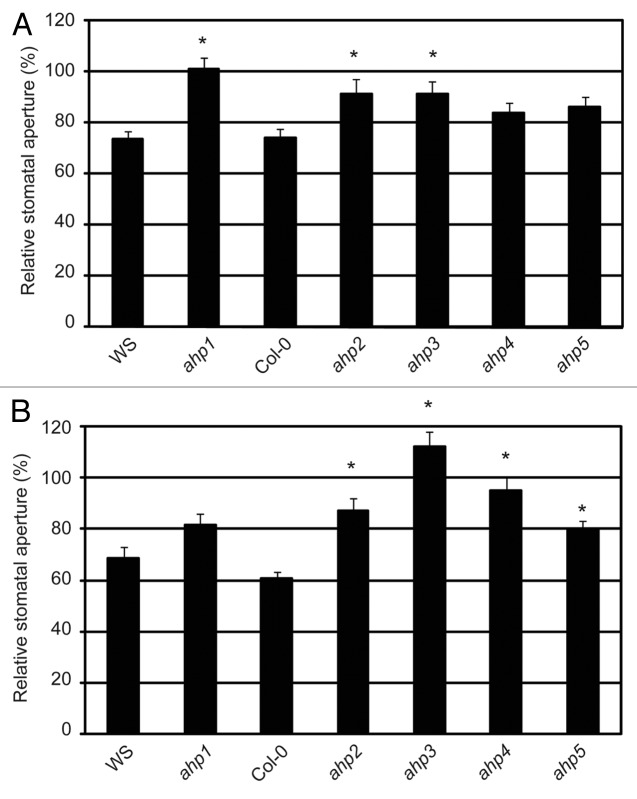
Figure 3. The ethylene and H2O2-induced stomatal response pathway downstream of AHK5. (A) Stomatal aperture in leaves of wild type (WS, Col-0) and different ahp Arabidopsis mutants. The leaves were exposed to 100 µM ethephon for 2h. Data are expressed as stomatal aperture response relative to mock-treated controls. Data are derived from measuring the apertures of at least 60 stomata from 3 independent experiments. * = Statistical difference (p-value ≤ 0.001 via Student’s t-test) compared with the wild type plants. (B) Stomatal aperture in leaves of wild type (WS, Col-0) and different ahp Arabidopsis mutants. The leaves were exposed to 100 µM H2O2 for 2h. Data are expressed as stomatal aperture relative to mock-treated controls. Data are derived from measuring the apertures of at least 60 guard cells from 3 independent experiments. * = Statistical difference (p-value ≤ 0.001 via Student’s t-test) compared with the wild type plants.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.