Figure 5. Model for clock effects on DNA damage-induced upregulation of p73 tumor suppressor.
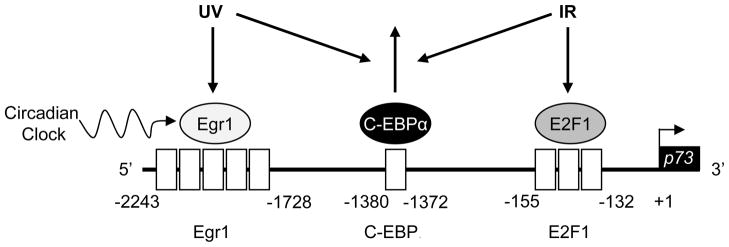
The 2 kb of the upstream sequence of the p73 promoter is shown in the direction 5′–3′, with the transcription start site indicated with a bent arrow. Functional transcription factor binding sites are indicated by open boxes, and the transcription factors are shown as circles. Transcription factor binding sites include: 5 early growth response-1 (Egr1) sites, 1 CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C-EBPα) site, and 3 E2F1 sites. Egr1 and E2F1 are transactivators, and C-EBPα functions as a repressor. Both UV and ionizing radiation (IR) cause dissociation of C-EBPα from the promoter. UV-induced upregulation of p73 is mediated by the clock controlled transcription factor Egr1. In contrast, IR-induced p73 upregulation is predominantly controlled by E2F1 which is not be affected by the circadian clock.
