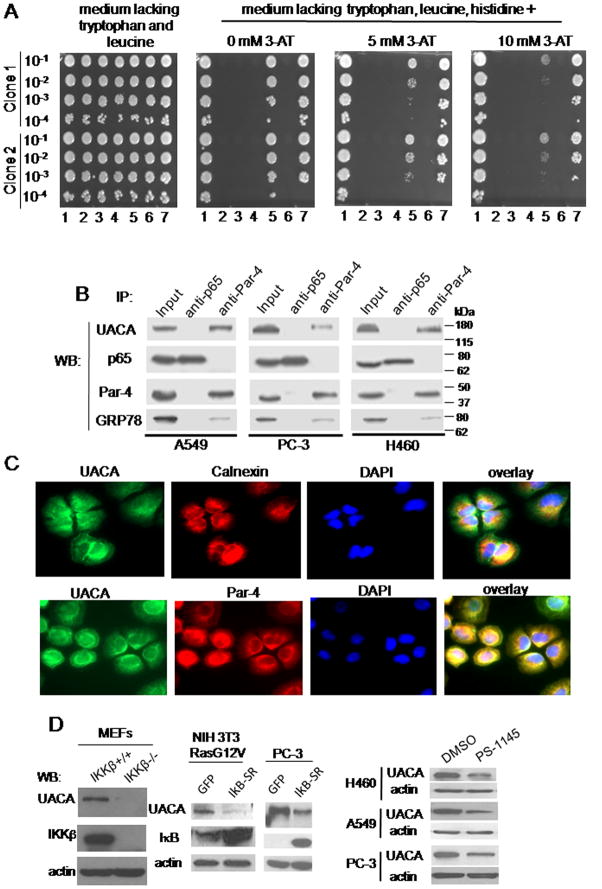
Figure 2. UACA binds to Par-4 and is regulated by NF-κB.
(A) UACA binds to Par-4 in one-on-one Y2H assay. Yeast cells were co-transformed with various constructs. 1: Positive Control (pB27-TCF4 and pP7-βcatenin); 2: Negative Control (pB27empty, which contains only the DBD; and pP7empty, which contains only the TA domain and is identical to pP6); 3: Negative Control (Par-4 + pP7empty); 4 : Negative Control (pB27empty + Sfrs11); 5 : Par-4 + Sfrs11; 6 : Negative Control (pB27empty + UACA); 7: Par-4 + UACA. The cells were then cultured in a 96-well plate; and the indicated serial dilutions were spotted on solid medium lacking tryptophan, leucine and histidine, and containing 0, 5, or 10 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (3AT). Sfrs11 is another prospective, albeit weaker, binding partner of Par-4. Interaction for two independent yeast clones is shown.
(B) UACA binds to Par-4 in human cell lines. Whole-cell lysates from the indicated cell lines were subjected to co-immunoprecipitation with Par-4 or p65/NF-κB (control) antibody. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot analysis. Lysates from each cell line were included as Input samples. UACA, ~160 kDa; p65, 65 kDa; Par-4, ~40 kDa; GRP78, ~78 kDa.
(C) UACA co-localizes with Par-4. H460 cells were subjected to ICC analysis for UACA (green fluorescence) and Par-4 (red fluorescence), or for calnexin (red fluorescence) and UACA (green fluorescence), and nuclei were stained with DAPI. The images were overlayed to determine co-localization (yellow fluorescence). Over 70 percent cells showed co-localization of Par-4 and UACA.
(D) NF-κB activity is essential for UACA expression. Western blot (WB) analysis for the indicated proteins was performed on whole-cell lysates from: MEFs from IKKβ−/− or IKKβ+/+ mice (left panel); NIH 3T3/Ras G12V or PC-3 cells infected for 18 h with IκB-SR adenovirus or GFP adenovirus (middle panels); or various cell lines treated with PS-1145 or DMSO for 24 h (right panels).