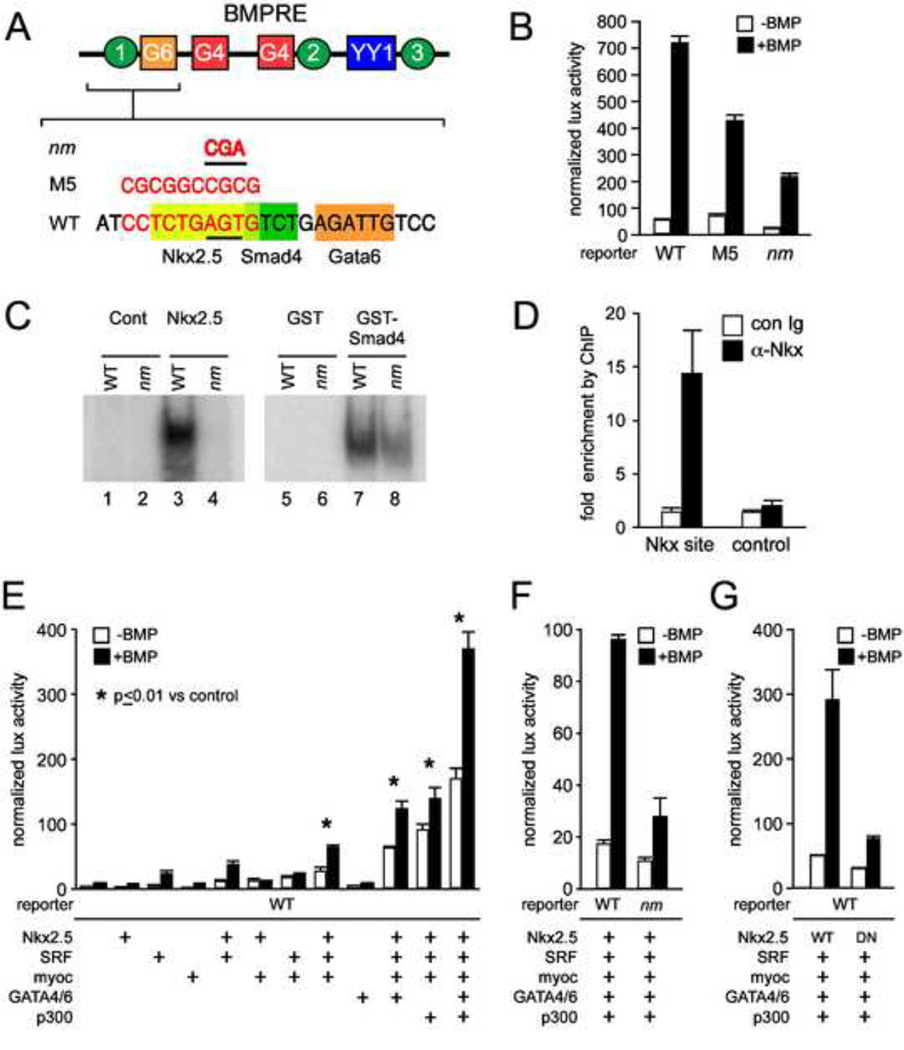
Figure 1. Nkx2.5 directly regulates the CNkx2.5-SHF enhancer.
A. A schematic of the 200 bp BMPRE of the chick Nkx2.5 gene depicting previously characterized Smad4 (green circles), GATA4/6 (red and orange squares) and YY1 (blue rectangle) binding elements is shown over an expanded view of nt 35–50 (Lee et al., 2004) which contains an Nkx2.5 binding consensus (yellow rectangle). The 10 bp M5 linker scanning mutation of BMPRE (nt 37–47) overlapping Nkx2.5 and Smad4 binding consensus sites is shown over the affected nucleotides in red, as is the smaller 3 bp mutation (designated Nkx2.5 mutant or nm) specifically targeting the Nkx2.5 binding element. B. BMP mediated reporter gene activation of wild-type Nkx2.5-lux-BMPRE reporter or reporter bearing the M5 or 3 bp nm mutations of the Nkx2.5 consensus site. The M5 mutation results in an approximately 50% decrease in BMP induced Nkx2.5-lux-BMPRE driven luciferase activity while the nm mutation results in a 4-fold decrease in luciferase activity. C. Data are shown for gel shifts performed with control (lanes 1 and 2), or Nkx2.5 cell extracts (lanes 3 and 4), or purified control GST (lanes 5 and 6) and GST-Smad4-MH1 domain proteins (lanes 7 and 8). Gel shifts were performed using double stranded oligonucleotides representing the wild-type BMPRE Nkx2.5 consensus (lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7) or the Nkx2.5 consensus bearing the nm mutation (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8). D. ChIP assay of Nkx2.5 binding to CNkx2.5-SHF-GFP reporter detects specific and selective enrichment (approx. 15 x) of amplicons from the BMPRE surrounding the Nkx2.5 binding consensus (Nkx site) using α-Nkx2.5 antibody vs. control IgG. No appreciable enrichment is observed of control GFP coding regions of the reporter (control). E. While addition of Nkx2.5 alone does not lead to a significant increase in CNkx2.5-SHF-lux luciferase activity in response to BMP (second column set from left), combinatorial addition of SRF, SRF cofactor Myocardin and cardiac GATAs 4 and 6 increases BMP activation of Nkx2.5-SHF-lux approximately 20-fold. The BMP response is further amplified 50–100 fold by addition of p300. F. CNkx2.5-SHF-lux response to Nkx2.5 and SRF, GATA4/6, SRF, Myocardin and p300 co-expression and BMP stimulation is reduced approximately 70% by site-specific mutation (nm) of the Nkx2.5 binding site on the CNkx2.5-SHF enhancer as compared to wild-type enhancer (WT). G. Multi-TF and BMP activation of the wild-type CNkx2.5-SHF-lux reporter is similarly reduced approximately 75% by use of a mutated non-DNA binding Nkx2.5 isoform (DN Nkx2.5) as compared to wild-type (WT Nkx2.5).