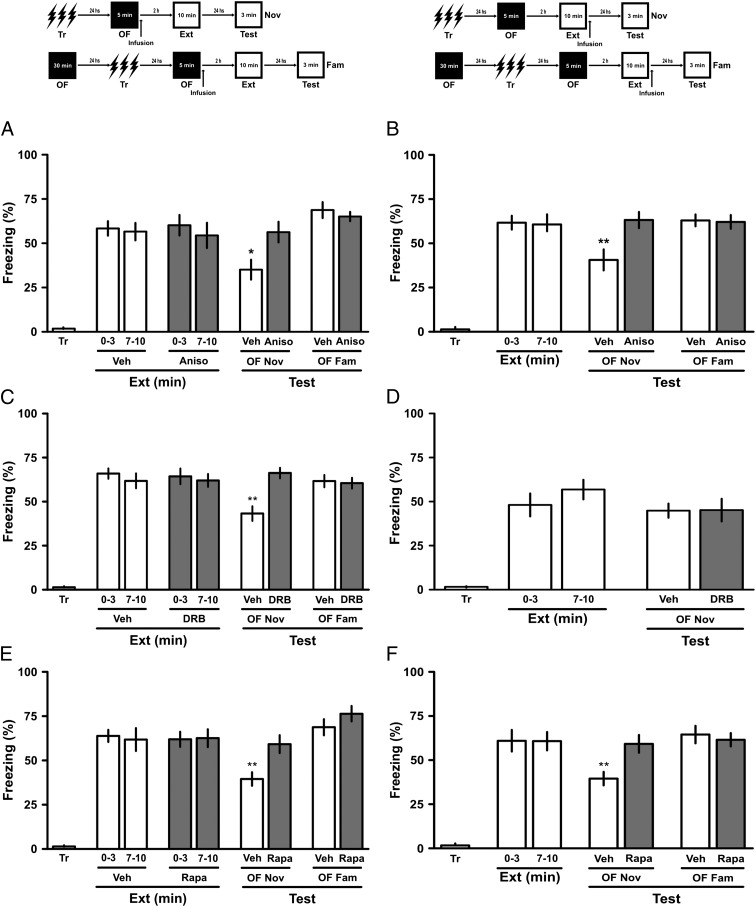
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of hippocampal protein synthesis can prevent the benefit of contextual novelty. (A and B) Rats with infusion cannulae implanted in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus were trained in a CFC task. After 24 h, they received intra-CA1 infusions of either vehicle (Veh) or anisomycin (Aniso; 80 μg per side) immediately after a 5-min exposure to a novel (Nov) or familiar (Fam) OF (A) or immediately after a weak extinction training session (B). After another 24 h, the animals were subjected to a 3-min retention test. *P < 0.05 vs. all groups in test sessions, Newman–Keuls test after one-way ANOVA. (C and D) Rats with infusion cannulae implanted in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus were trained in a CFC task. After 24 h, they received intra-CA1 infusions of either vehicle (Veh) or DRB (8 ng per side) immediately after a novel or familiar OF (C) or immediately after a weak extinction training session (D). After another 24 h, the animals were subjected to a 3-min retention test. *P < 0.05 vs. all groups in test sessions, Newman–Keuls test after one-way ANOVA. (E and F) Rats with infusion cannulae implanted in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus were trained in a CFC task. After 24 h, they received intra-CA1 infusions of either vehicle or rapamycin (Rapa; 5 pg per side) immediately after a 5-min exposure to a novel or familiar OF (E) or immediately after a weak extinction training session (F). After another 24 h, the animals were subjected to a 3-min retention test. *P < 0.05 vs. all groups in test sessions, Newman–Keuls test after one-way ANOVA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of the percentage of time spent freezing. n = 11 or 12 animals per group. (Upper) Schematic representation of the behavioral protocol used.