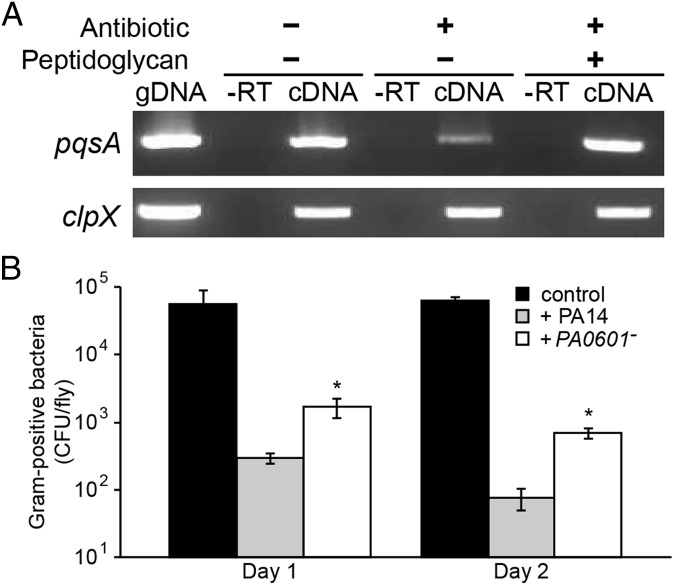
Fig. 3.
(A) Decreased levels of the pqsA transcript in antibiotic-treated Drosophila. Reverse transcriptase PCR was used to examine pqsA transcript levels during Drosophila infection under three conditions: (i) no antibiotic treatment of flies and no peptidoglycan added; (ii) antibiotic-treated flies with no peptidoglycan added; (iii) antibiotic-treated flies with peptidoglycan added. gDNA is the genomic DNA positive control, and −RT is the negative control using RNA as the PCR template. The constitutively expressed clpX gene was used as a control. A representative ethidium bromide stained agarose gel is shown. (B) P. aeruginosa colonization reduces the native Gram-positive flora of Drosophila. Gram-positive bacteria were enumerated by viable counts on phenylethyl alcohol agar. Shown are cfu per fly from uninfected flies (control), and flies infected with either WT P. aeruginosa (PA14) or the PA0601 mutant (PA0601−). *P < 0.01 by Student t test compared with PA14-infected flies. Error bars represent SD, n = 3.