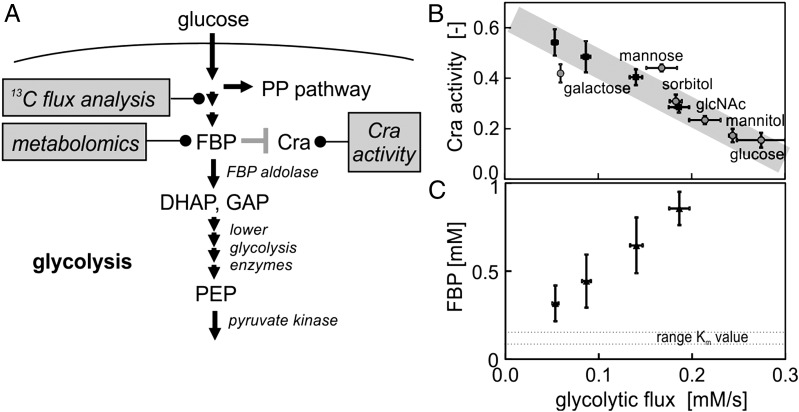
Fig. 1.
(A) Schematic illustration of the proposed flux sensor, its embedding in the glycolytic pathway, and the experimental methods used. (B) Cra activity as a function of glycolytic flux (at the FBP aldolase reaction) in glucose-limited chemostat cultures (black squares) and batch cultures (gray circles) with different carbon sources (glcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine). Cra activity is defined as the fraction of time that Cra spends bound to the promoter—in this case the pykF promoter, which is solely repressed by Cra (53). All substrates with the exception of galactose are substrates that are transported into the cell via the phosphotransferase system using phosphoenolpyruvate as cosubstrate. (C) FBP concentration as a function of glycolytic flux in glucose-limited chemostat cultures. All measurements were done in triplicate, and errors bars represent 1 SD.