Fig. 3. GSH is a continuous source of cysteine via the γ-glutamyl cycle.
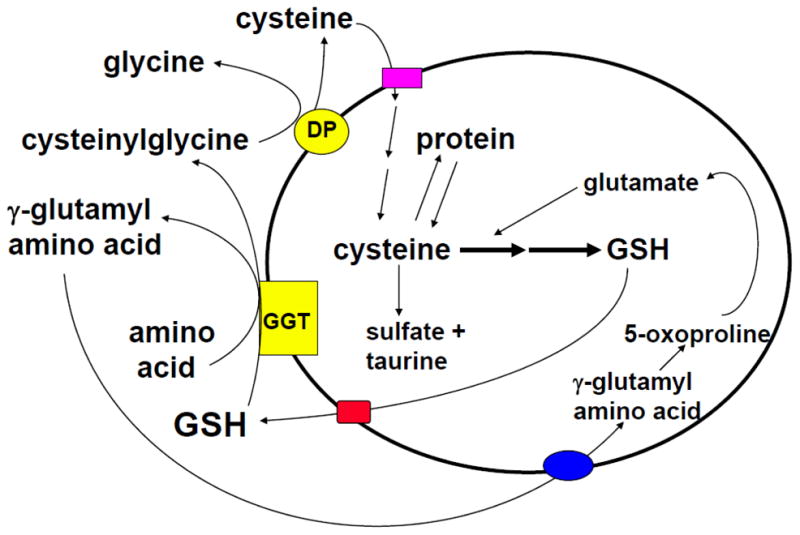
GSH is transported out of the cell where the ecto-enzyme γ-glutamylpeptidase (GGT) transfers the γ-glutamyl moiety of GSH to an amino acid (the best acceptor being cystine), forming γ-glutamyl amino acid and cysteinylglycine. The γ-glutamyl amino acid can then be transported back into the cell and once inside, the γ-glutamyl amino acid can be further metabolized to release the amino acid and 5-oxoproline, which can be converted to glutamate and reincorporated into GSH. Cysteinylglycine is broken down by dipeptidase (DP) to generate cysteine and glycine, which are also transported back into the cell to be reincorporated into GSH. Most of the cysteine taken up is incorporated into GSH while the rest is incorporated into newly synthesized proteins and/or broken down into sulfate and taurine.
