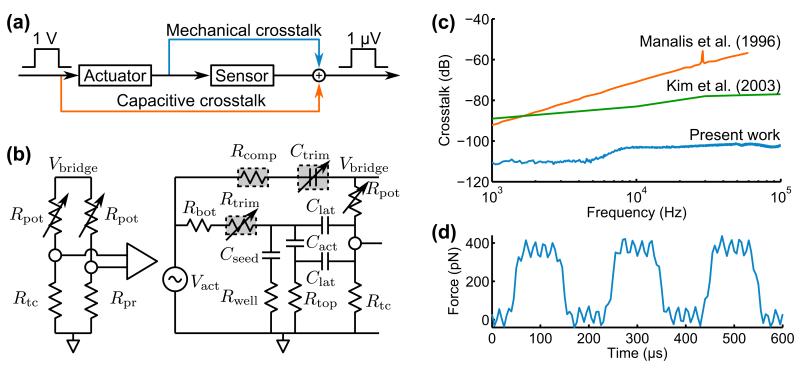
Figure 3.
Actuator-sensor crosstalk. (a) The piezoelectric actuator is mechanically and capacitively coupled to the piezoresistive sensor. The sensor noise floor is 120 dB smaller than the typical actuator control signal. (b) Crosstalk is converted to a common-mode signal through differential piezoresistor readout. A potentiometer and variable capacitor are used to trim mismatch between the main and compensation force probes. (c) The resulting performance is a 20 dB improvement over prior work and is limited to -115 dB by mechanical crosstalk. (d) Example of piezoresistive readout from a compensated force probe applying a 350 pN force to a hard silicon sample in air with a rise time of 10 μs and RMS force noise of 13 pN.