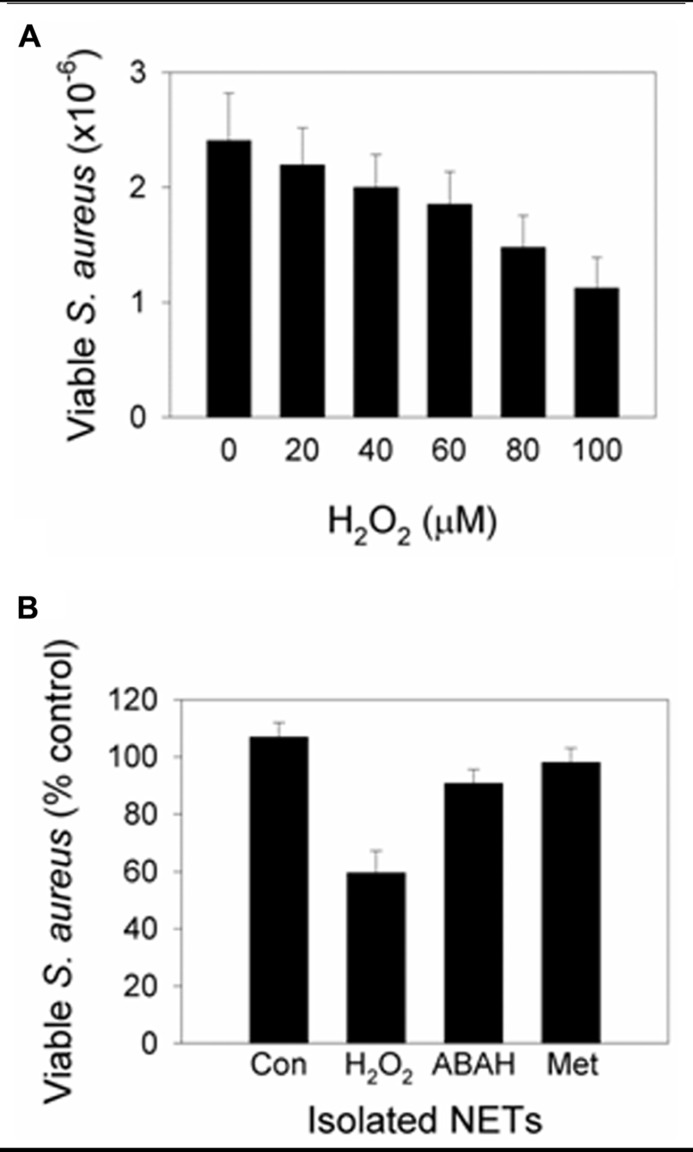
FIGURE 2.
Addition of H2O2 to NETs induces MPO-dependent killing. Neutrophils were stimulated with PMA to form NETs then incubated with S. aureus in the presence or absence of (A) varying concentrations of H2O2 or (B) 100 μM H2O2 (added in 20 μM aliquots every 5 min to facilitate MPO turnover). At the examined concentrations, H2O2 in the absence of NETs had no significant effect on S. aureus viability. (A) Bacterial numbers significantly decreased with ≥40 μM H2O2 (p< 0.05, t-test on normalized data, n = 3). (B) Bacterial viability decreased with H2O2 (p< 0.001), and inhibition of MPO with ABAH and scavenging of HOCl with methionine (Met) prevented killing (p< 0.01; one-way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak pairwise comparison, n = 5). Results are presented as percent of control cells (Con) incubated with NETs alone. Data obtained with permission from Parker et al. (2012a).