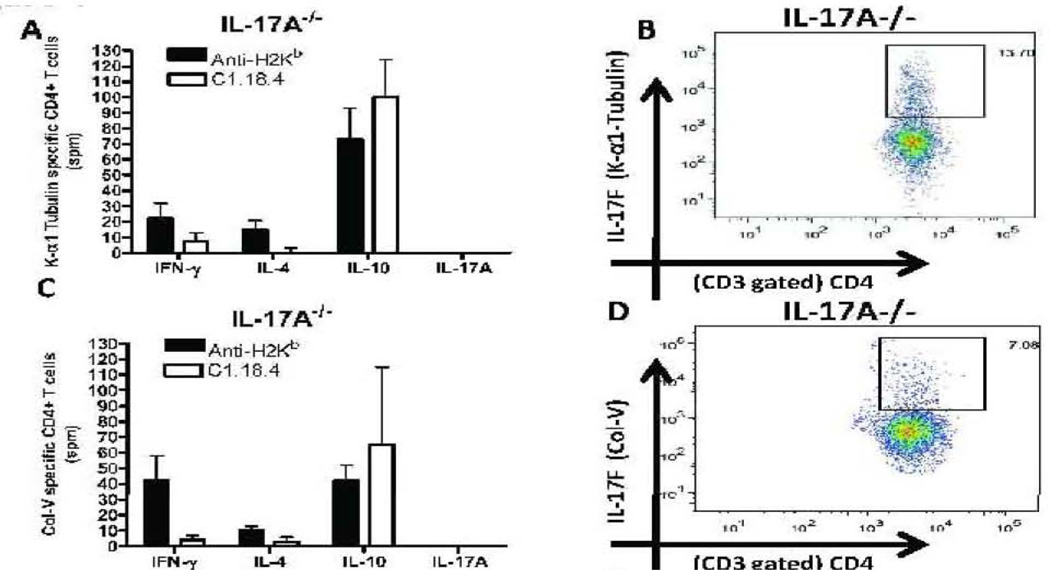
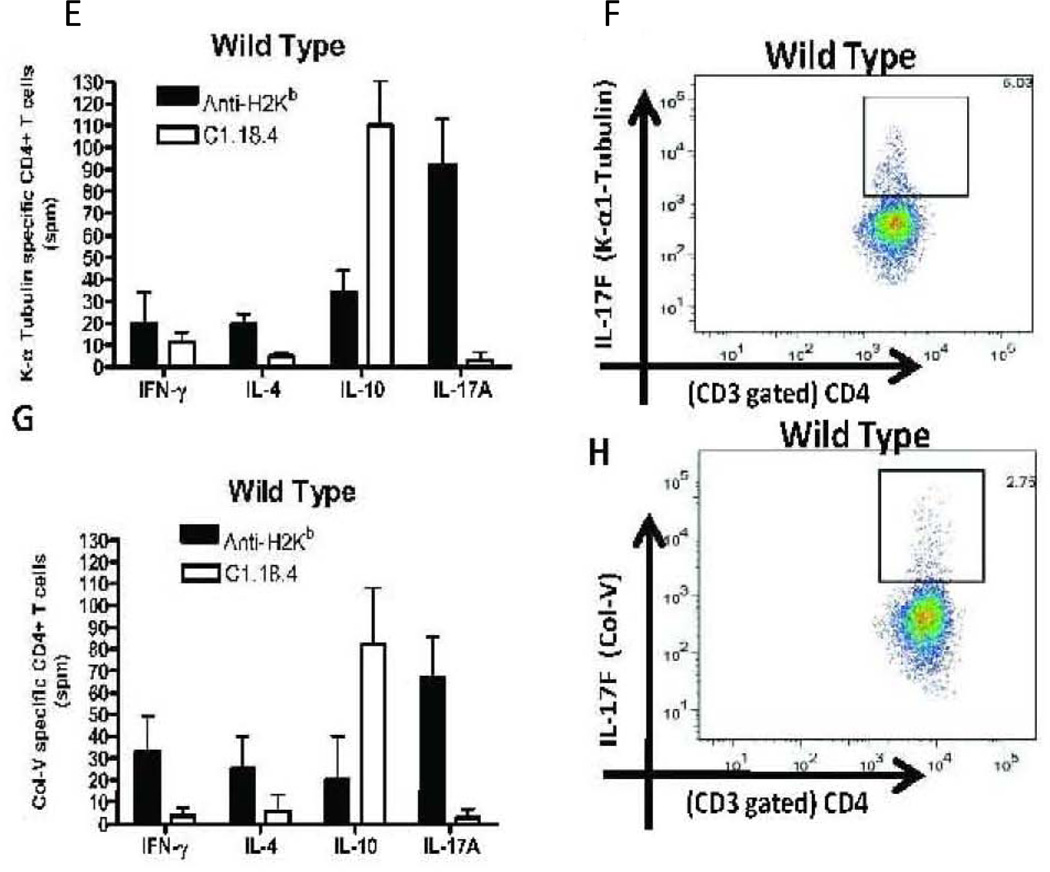
Figure 3. Induction of autoreactive CD4+ T cells which predominantly secrete IL-17A and IL-17F following administration of anti-MHC Class I Abs.
Lung infiltrating T cells were isolated from the lungs of IL17A −/− and wild type mice treated with anti-H2Kb or control antibody (n=5 each, the figures shown are a representative of 5 mice). The frequency of T cells secreting IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17A and IL-10 specific to KAT and Col-V were measured by ELISPOT (Figure 3, A,C,E,G) and presented as means ± SD. The frequency of IL-17F secreting CD4+ T cells specific to self antigens were determined by flow cytometry (Figure 3, B,D,F,H). A significant increase in the frequency of IL-17A secreting CD4+ T cells specific to KAT and Col-V was observed in the lungs of anti-H2kb treated WT mice compared to control animals. An increased frequency of IL17F secreting CD4+ T cells specific to KAT (IL-17A−/−:13.70% vs WT: 5.03%) and Col-V (IL-17A−/:7.08% vs WT: 2.75%) was noted in anti-H2Kb treated IL-17A−/− mice compared to WT mice. No significant difference was seen in the levels of IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-10 secreting CD4+ T Cells specific to KAT and Col-V was seen between IL-17A−/− and WT administered with anti-H2kb.