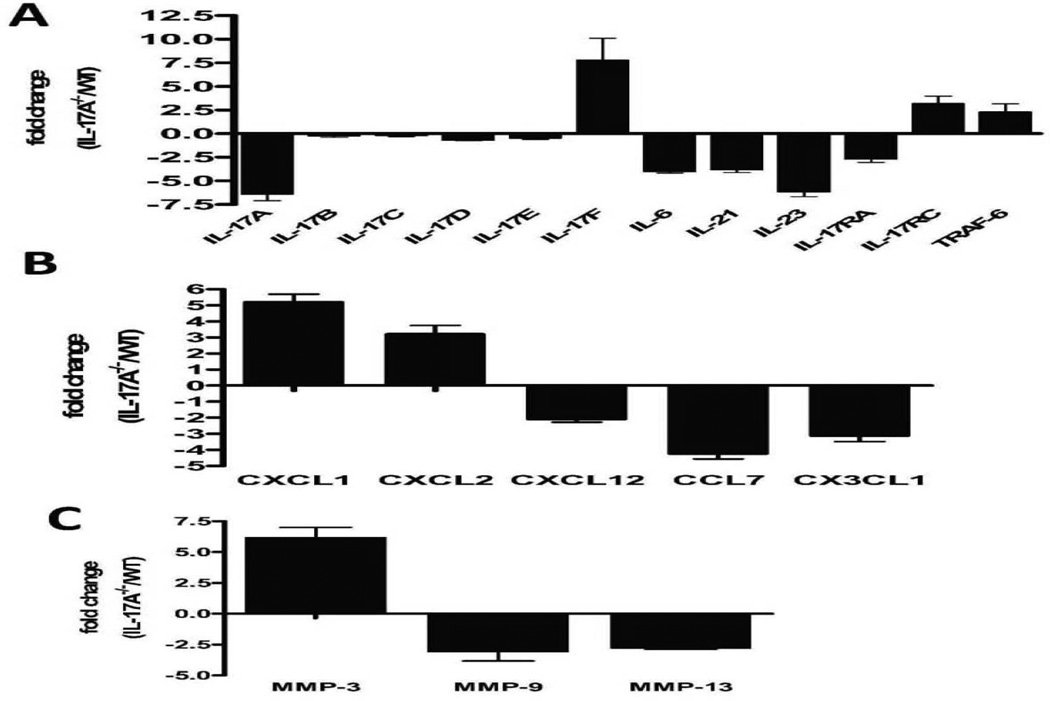
Figure 4. Increased induction of IL-17A and IL-17F mediated inflammatory cascades following anti-MHC class I administration.
Total RNA from the lungs of anti-H2KB treated WT and IL-17A−/− were extracted using Trizol reagent and used for the expression profile of the signaling cascades intermediates in the autoimmunity pathway using autoimmunity PCR array. The samples were normalized using housekeeping gene expression and the results are expressed as fold expression observed in IL17A −/− mice over expression observed in WT mice. Anti-H2Kb administration in IL-17A−/− resulted in significant increase in levels of IL-17F (7.80 fold) but not IL-17A (−6.4 fold), IL-17B (−0.28 fold), IL-17C (−0.23 fold), IL-17D (0.70 fold), IL-17E (−0.49 fold), IL-6 (−4.01 fold), IL-21(−3.84 fold) and IL-23(−6.18 fold) compared to WT. Anti-H2Kb administered IL-17A−/− demonstrated a significant increase in levels of IL-17RC (3.2 fold) and TRAF-6 (2.3 fold) but not IL-17RA (−2.70 fold). Anti-H2Kb administered IL-17A−/ demonstrated a significant increase in the levels of CXCL1 (5.2 fold), CXCL2 (3.2 fold) and a significant reduction in the levels of CXCL12 (−2.10 fold), CCL7 fold (−4.24 fold) and CX3CL1 (−3.12 fold). Anti-H2Kb administered IL-17A−/− demonstrated differential induction of MMP-3 (6.2 fold), MMP-9 (−3.1 fold) and MMP-13 (−2.8 fold).