Figure 4.
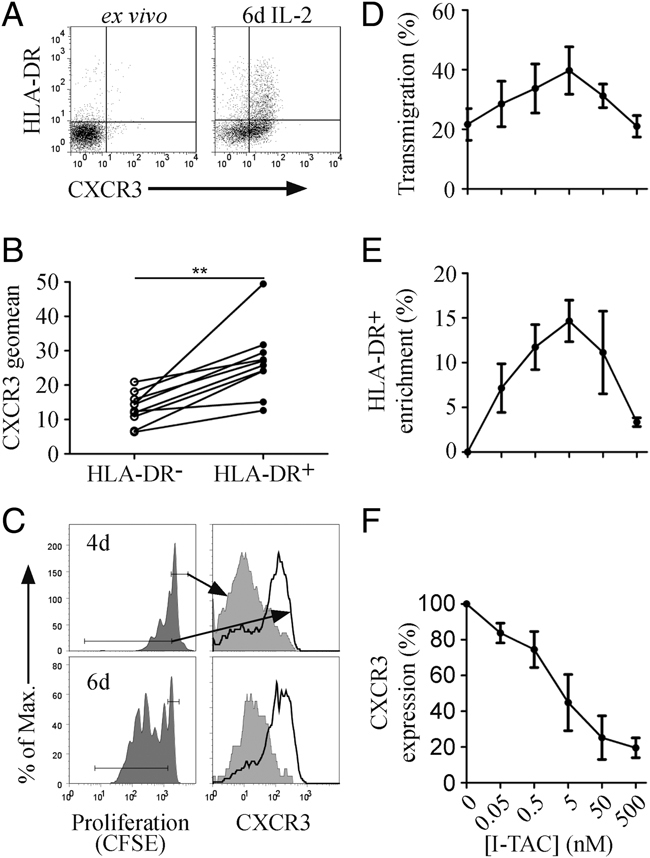
HLA-DR+ NK cells express a functional chemokine receptor CXCR3. (A) NK cells from one donor ex vivo (left) and after 6 days culture with IL-2 (right) were analysed by flow cytometry for expression of HLA-DR and CXCR3. (B) NK cells cultured with IL-2 for 6 days were analysed by flow cytometry for expression of HLA-DR and CXCR3. The intensity (geomean) of CXCR3 expression was compared between HLA-DR− and HLA-DR+ populations. (C) Comparison of CXCR3 expression (right) on non-proliferating (grey shaded) and proliferating (black) NK cells as gated in the CFSE histogram (left). (D) NK cells from three donors were cultured with IL-2 for 6 days, then assessed for their chemotactic response to the CXCR3 ligand I-TAC in a transmigration chemotaxis assay. The percentage of NK cells that responded was calculated by haemocytometer — counting the cells in the lower chamber. (E) The transmigrated cells were also analysed by flow cytometry for expression of HLA-DR, plotted as the enrichment of HLA-DR+ NK cells in the transmigrating cells, relative to the buffer control, and (F) expression of CXCR3 on transmigrated NK cells. (D–F) n=3, median±range.
