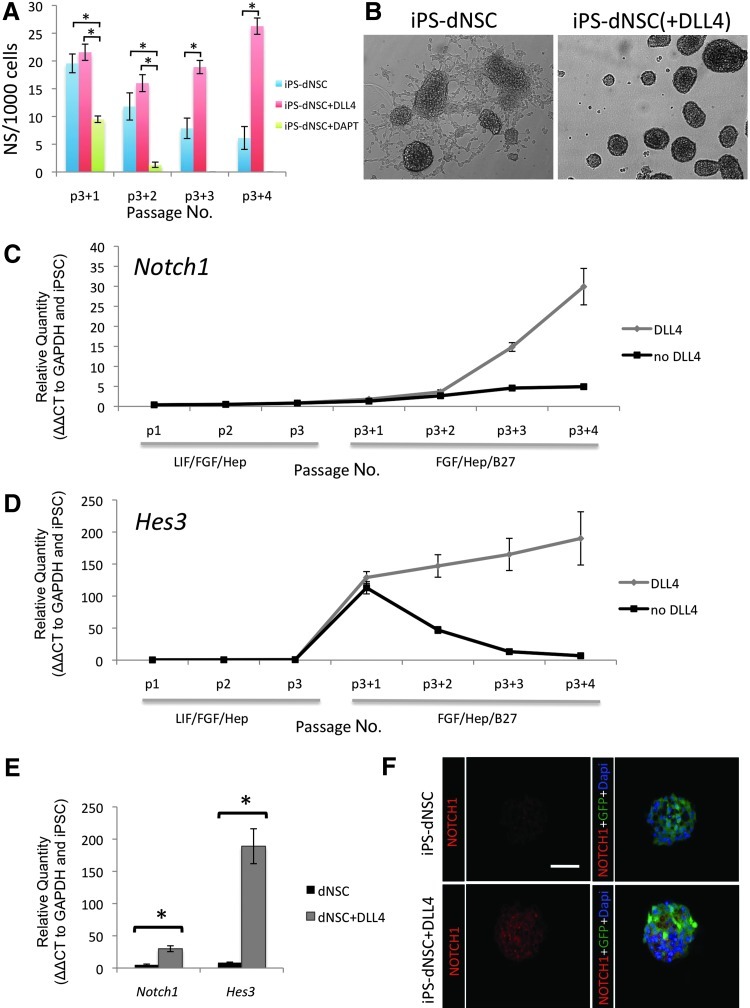
FIG. 3.
The addition of DLL4 significantly increased NOTCH pathway genes in iPS-dNSCs. (A) The number of neurospheres per 1,000 cells in definitive media conditions alone, with DLL4 or with DAPT was evaluated. The addition of the NOTCH pathway inhibitor DAPT resulted in significantly fewer neurospheres and failure to form spheres beyond the second passage. Significantly more definitive neurospheres were formed in the presence of DLL4. (B) Phase-contrast microscopy images of passage 4 iPS-derived definitive neurospheres (left) and iPS-derived definitive neurospheres with DLL4 (right). The iPS-derived definitive neurospheres show a considerable amount of adhesion and differentiation compared to iPS-derived definitive neurospheres cultured with DLL4. [(C, E) left] Notch1 gene expression is significantly increased in iPS-dNSCs by the fourth passage in definitive conditions with DLL4 in the media compared to the definitive media alone. [(D, E) right] HES3, a downstream mediator of NOTCH, increases in iPS-dNSCs with a single passage in definitive media regardless of DLL4 treatment, however, without exogenous DLL4 treatment, HES3 expression returns to baseline levels by passage 4. (F) Immunolabeling for receptor Notch1 on cryopreserved definitive neurospheres with and without DLL4 agonism. C5-4A iPSC line. mean±SEM; n=4–5, *P<0.05 scale bar represents 75 μm. DLL4, Delta-like ligand 4; DAPT, N-[N-(3,5-Difluorophenacetyl)-L-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester.