Figure 2.
Conservation of Residues and Motifs in FF Proteins from Nematodes
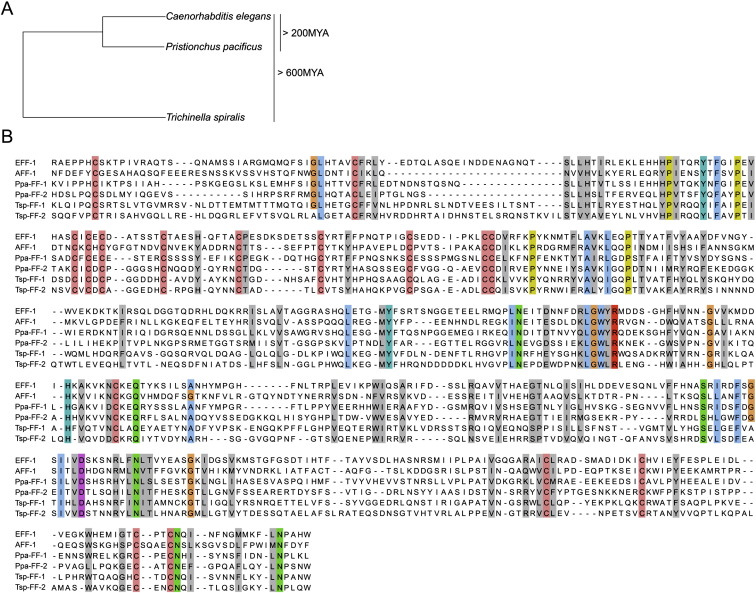
(A) Phylogeny of nematode species used for the sequence alignment. Using BLAST, FF proteins were identified in 17 nematode species from different clades (O.A. and B.P., unpublished data). We aligned Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce) FF proteins with putative homologs from Pristionchus pacificus (Ppa), estimated to diverge 200 million years ago (MYA) (Gutierrez and Sommer, 2004), and with proteins from the remotest nematode wherein FF proteins have been identified so far, the parasite Trichinella spiralis (Tsp) (divergence estimated more then 600 MYA; Mitreva and Jasmer, 2006).
(B) Extracellular domains of FF proteins without signal sequences were aligned using the Jalview software (Clamp et al., 2004). Conservation of cysteines (pink), the LGWYR motifs, and partial conservation of prolines (yellow) suggests functional roles for these residues and motifs (Sapir et al., 2007). Color is shown in residues of 100% conservation and gray in cases where 50% of the physicochemical properties are conserved (Livingstone and Barton, 1993). Accession numbers: CeAFF-1: EF205023; CeEFF-1: C26D10.5 PpaFF-1: contig162.29; PpaFF-2: Contig735.1 P. pacificus california “Assembly Freeze 1.” TspFF-1: Contig1.317; TspFF-2: Contig3.96 Trichinella spiralis-1.0-contigs.