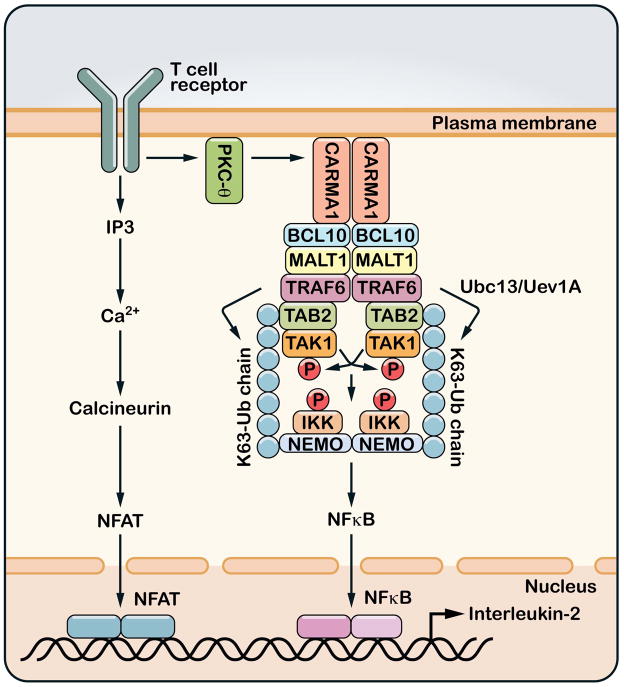
Figure 3. Ubiquitination and T cell activation.
Upon engagement of MHC-bound peptides, T cell receptors (TCR) trigger a cascade of tyrosine phosphorylation events that lead to the activation of protein kinase C-θ (PKCθ). PKCθ then phosphorylates the membrane-associated protein CARMA1, which in turn recruits BCL10 and MALT1. MALT1 binds to TRAF6 and perhaps other ubiquitin E3 ligases. The binding of MALT1 to TRAF6 induces TRAF6 oligomerization and activates its E3 ligase activity, which then catalyzes K63 polyubiquitination to activate TAK1 and IKK. T cell receptor signaling also activates the calcineurin – NFAT pathway through increasing the intracellular concentration of calcium. NFAT, NF-κB and other transcription factors cooperate in the nucleus to induce the production of interleukin-2 (IL-2).