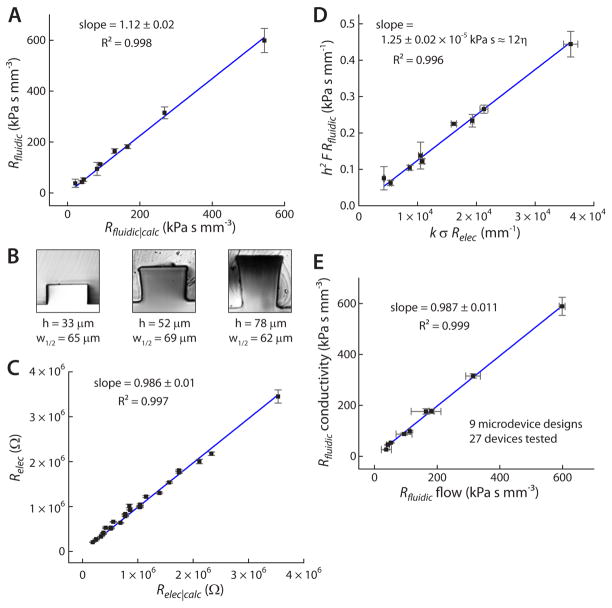
Figure 2.
A) Rfluidic (measured) was shown to be well-correlated with Rfluidic|calc for all of the nine tested fluidic resistors. B) Cross-sections of PDMS channels were sliced with a razor and imaged, revealing the slightly distorted rectangular cross-section, particularly in the deeper channels. C) Measured Relec was well-correlated with Relec|calc for all nine fluidic resistors and with three different conductivity standards (27 values of Relec). D) A plot of h2 F Rfluidic versus k σ Relec gave a slope of 1.25 × 10−5 ± 0.02 kPa s−1, essentially equal to 12 η = 1.21 × 10−5 kPa s−1, as expected from Eq. 5. This result was obtained after triplicate measurements on 27 different microdevices. E) A comparison between the meniscus tracking method (Rfluidic flow) and the new conductivity-based method (Rfluidic conductivity) showed excellent correlation, with lower error rates associated with the more straightforward conductivity-based method.