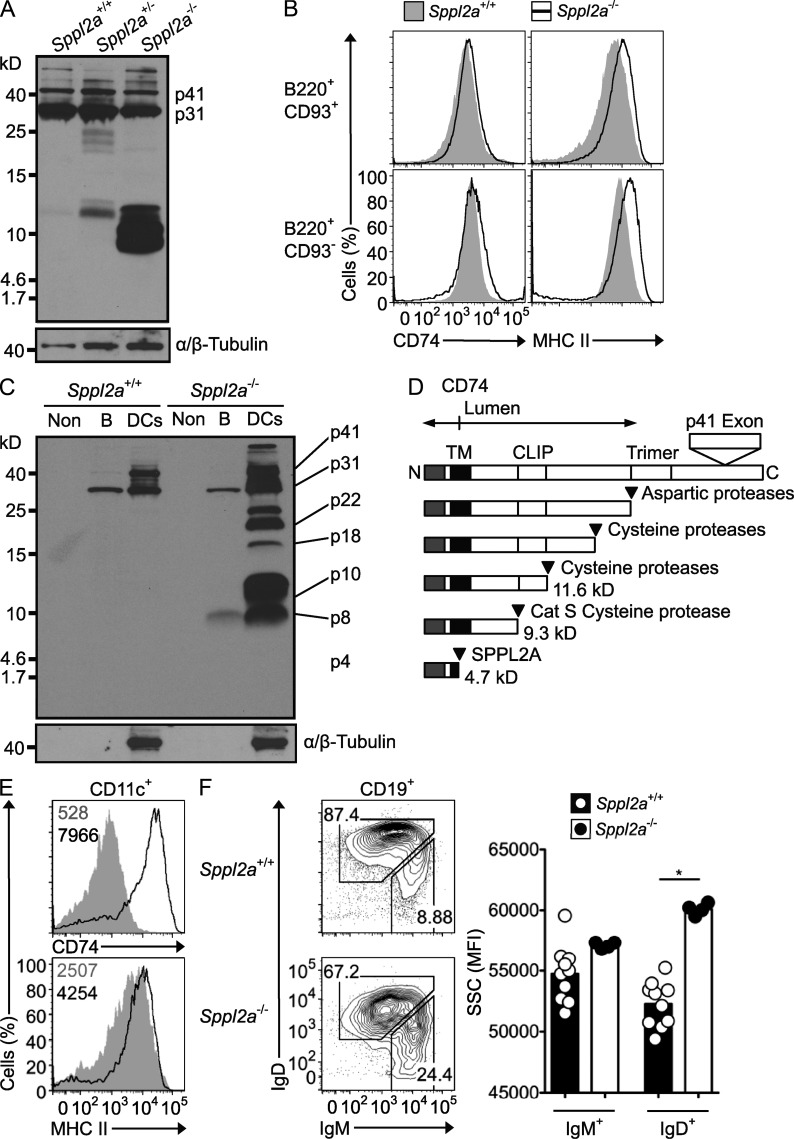
Figure 4.
Proteolytic processing and intracellular retention of CD74 requires SPPL2A. (A) Immunoblot analysis of splenic B cells from Sppl2a−/−, Sppl2a+/−, and Sppl2a+/+ mice. Blots were probed with In-1 antibody against the CD74 N-terminal tail and then stripped and reprobed with antibody to α/β-Tubulin. p41 and p31 isoforms of CD74 are indicated. (B) Flow cytometric staining for cell surface MHC II and CD74 on splenic B220+CD93+ immature and B220+CD93− mature B cells from Sppl2a+/+ (shaded gray) and Sppl2a−/− mice (black line). (C) Immunoblot analysis of splenic B cells and the non-DC/non-B cell (Non) fraction from Sppl2a−/− and Sppl2a+/+ mice probed as for A. (D) Schematic diagram of CD74 processing steps and products, showing estimated molecular mass (kilodaltons) and proteases involved. (E) Flow cytometric staining for cell surface MHC II and CD74 on splenic CD11c+ DCs from Sppl2a+/+ (shaded gray) and Sppl2a−/− mice (black line). Numbers in the plots indicate geometric mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (F) Flow cytometric light SSC as a relative measure of cell vesicle content, gated on IgMhigh immature and IgD+ mature B cells in the blood as shown in the left panel of plots from Sppl2a+/+ and Sppl2a−/− mice. Bars show mean, and each symbol is data from one mouse. P-value from one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s Multiple Comparison posttest: *, P = 0.01–0.05. Data are representative of one experiment (A–C) or at least three experiments with three or more mice per group (E and F).