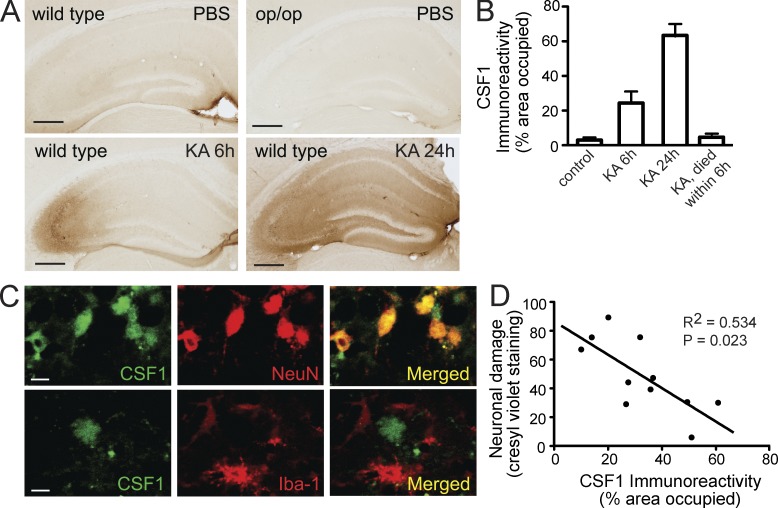
Figure 5.
Endogenous CSF1 is up-regulated in neurons after excitotoxic brain injury. (A–C) Wild-type FVB/N or CSF1-null Csf1op/op mice (2 mo old) were lesioned with 20 mg/kg KA (subcutaneous injection) and sacrificed 6 h, 1 d, and 3 d later. Brain sections were immunostained with an antibody against CSF1. (A) Representative images from wild-type controls (no injury), KA lesioned and sacrificed at 6 h, KA lesioned and sacrificed at 24 h, or Csf1op/op mice. (B) Quantification of CSF1 immunoreactivity in the hippocampus after KA injury (n = 4–6 mice/group). Error bars indicate SEM. (C) Colocalization of CSF1 and neuronal marker NeuN but not microglial marker (Iba-1) after KA lesion (6 h). Bars: (A) 200 µm; (C) 20 µm. (D) Inverse correlation (Pearson correlation) of CSF1 immunoreactivity with excitotoxic injury assessed by cresyl violet staining. Results are from one out of two independent experiments.