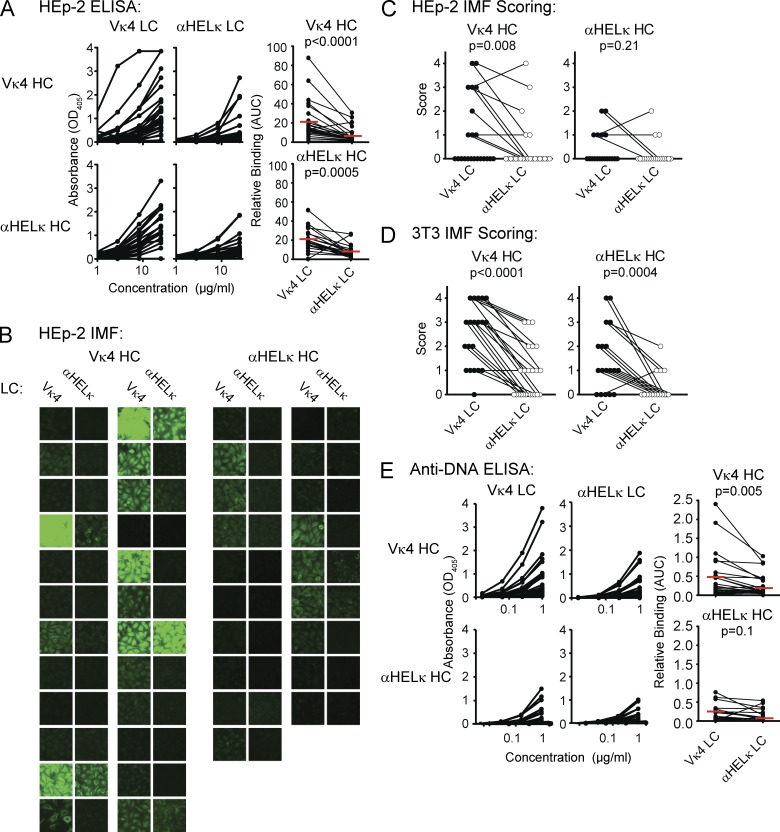
Figure 2.
A mouse model of selection in the context of a polyclonal repertoire. (A) Recombinant mAbs were expressed from pairing different HC genes of the B220+AA4− mature mCκ+hCκ− B cells isolated from IgκVκ4/h mice (a total of 24 VH genes; top) or Igκαhel/h mice (a total of 19 VH genes; bottom) with vectors containing either the Vκ4 or αHELκ LC genes. Each pair of antibodies sharing the same VH gene was tested simultaneously. ELISA binding curves are shown in the left (VH/Vκ4 antibodies) and middle (VH/αHELκ antibodies) panels. Each dot in the right panel represents the area under the binding curve (AUC) of one mAb. The red line indicates the mean value for that group. (B and C) Binding to HEp-2 cells by IMF of mAbs described in A. Shown are representative images of cell binding of each antibody (B) and pairwise comparison of the mode of IMF intensity of each VH gene paired with the Vκ4 or αHELκ LC (C) scored on a scale of 0–4 (whole numbers only). (D) Antibody binding to 3T3 cells detected and scored in the same manner as HEp-2 cells in C. (E) dsDNA binding by ELISA of antibodies described in A and analyzed as in A. Antibodies with shared VH genes were paired both for comparing ELISA binding curves (AUC) and for scoring HEp-2 IMF. Statistical significance was calculated using the paired Student’s t tests. Shown are representative data of at least three independent experiments.