Abstract
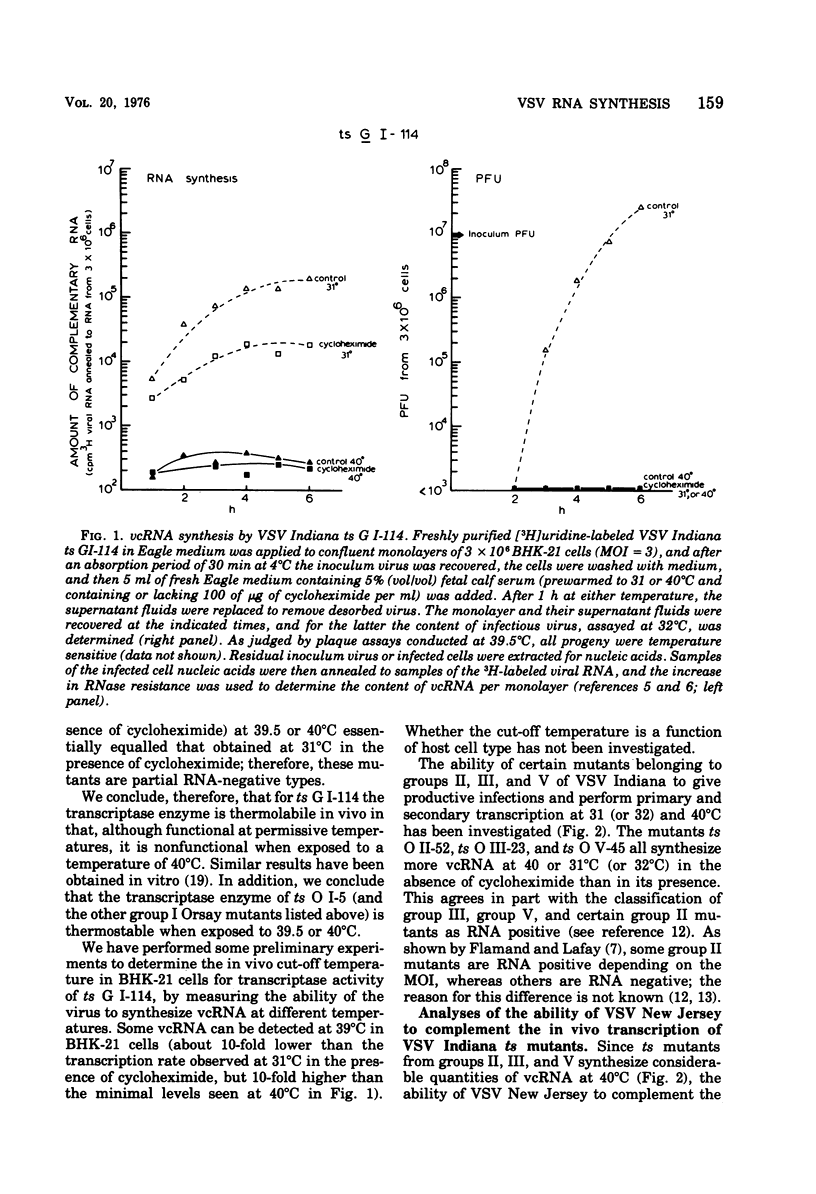
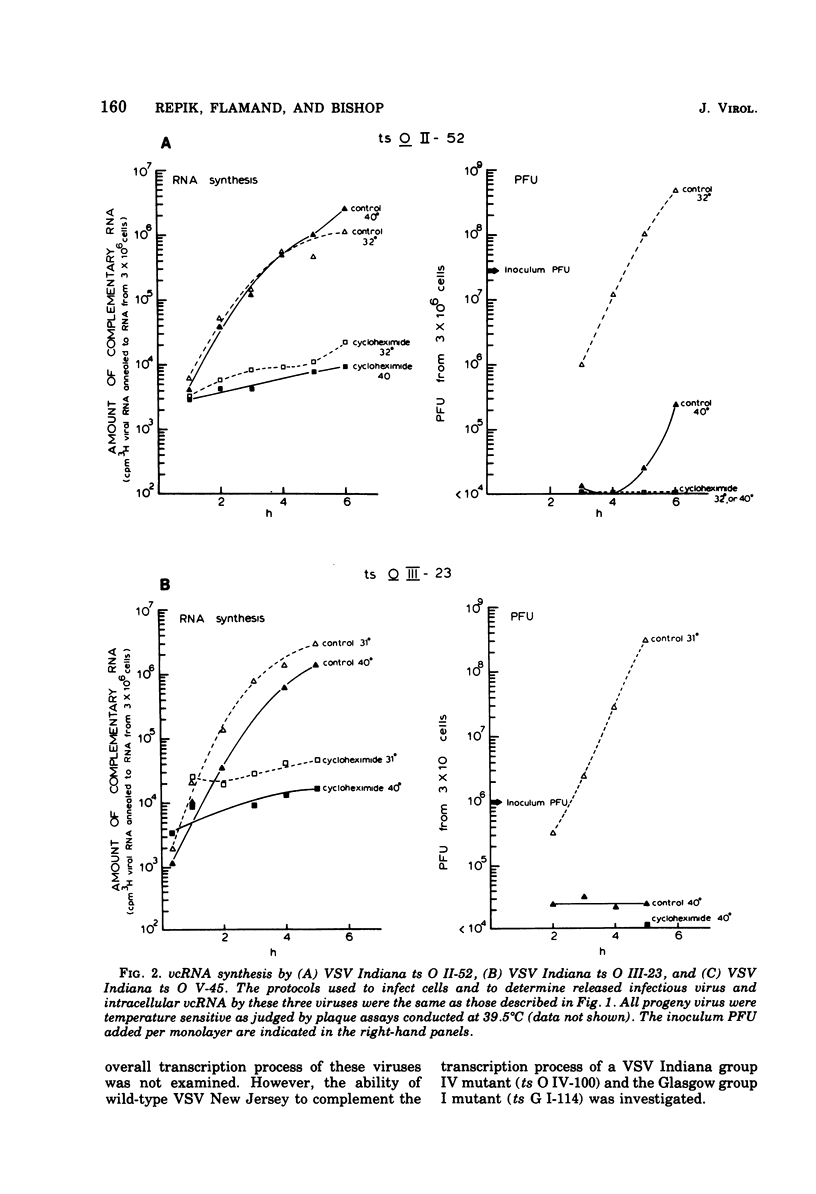
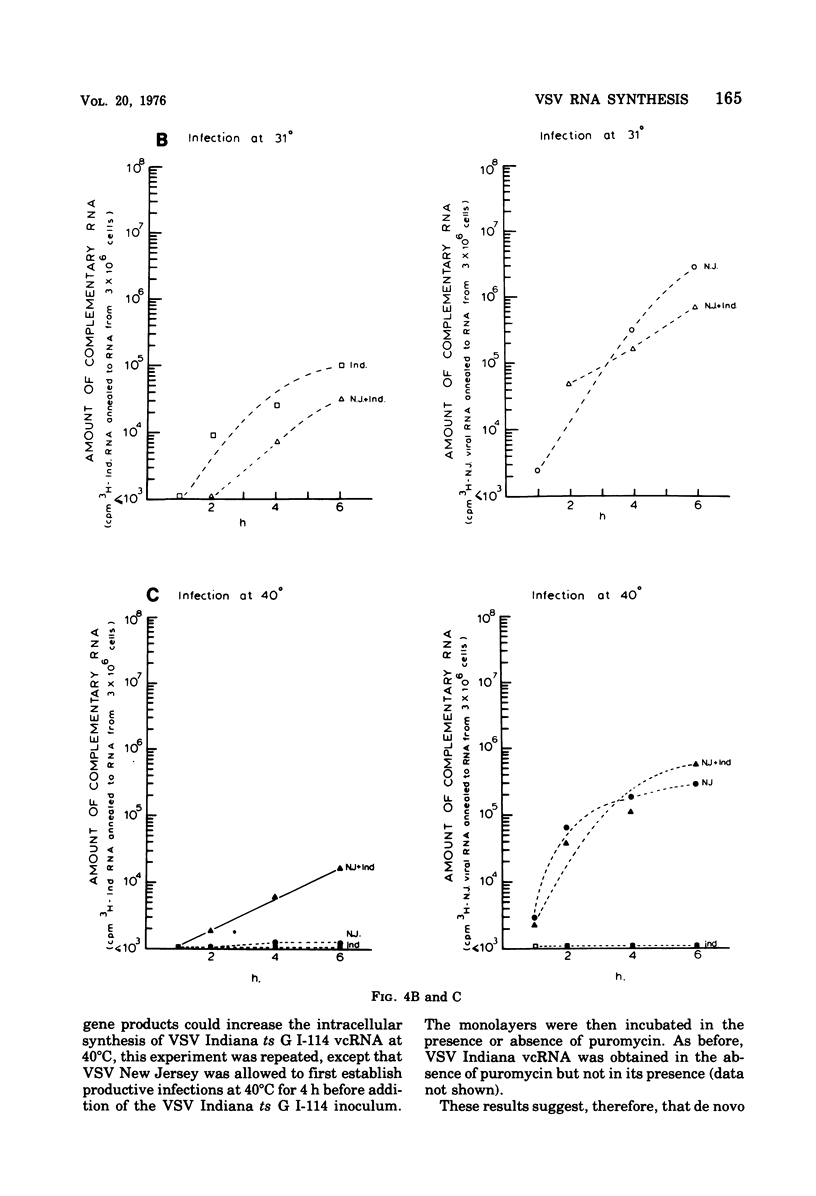
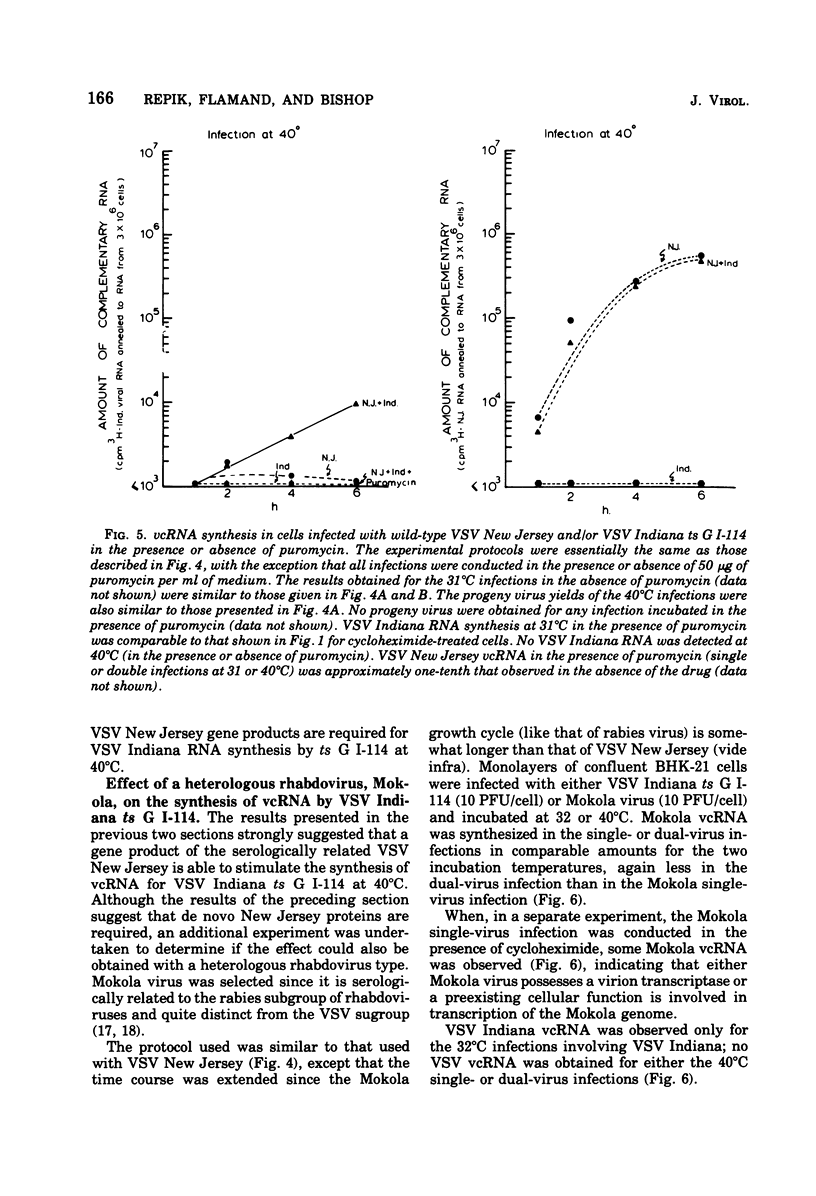
The ability of certain vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV; Indiana serotype) temperature-sensitive (ts) mutants to synthesize intracellular viral complementary RNA (vcRNA) at permissive or nonpermissive temperatures for productive infections has been investigated. Mutants belonging to complementation groups II, III, and V synthesize RNA at nonpermissive temperature in amounts essentially equivalent to that obtained at permissive temperatures. Mutant ts G I-114 possesses a thermolabile transcriptase and does not synthesize vcRNA at 40 degrees C; however, mutants ts O I-5, O I-53, O I-78, and O I-80 possess thermostabile transcriptases that are capable of some vcRNA synthesis at 40 degrees C. All five group I mutants are defective in their secondary transcription ability at 40 degrees C. Wild-type VSV New Jersey virus is able to complement the transcription defect of ts G I-114 at 40 degrees C. This complementation is inhibited by puromycin, suggesting that a viral gene product of VSV New Jersey (e.g., its transcriptase or a transcriptase component) is involved. Mokola virus is not able to complement the ts G I-114 defect, although Mokola does synthesize vcRNA in infected cells (in the presence or absence of cycloheximide).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop D. H., Emerson S. U., Flamand A. Reconstitution of infectivity and transcriptase activity of homologous and heterologous viruses: vesicular stomatitis (Indiana serotype), Chandipura, vesicular stomatitis (New Jersey serotype), and Cocal viruses. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):139–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.139-144.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Brown F. Serological relationships between different strains of vesicular stomatis virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Sep;16(3):391–398. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-16-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Yu Y. Both NS and L proteins are required for in vitro RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1348–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1348-1356.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federer K. E., Burrows R., Brooksby J. B. Vesicular stomatitis virus--the relationship between some strains of the Indiana serotype. Res Vet Sci. 1967 Jan;8(1):103–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A., Bishop D. H. In vivo synthesis of RNA by vesicular stomatitis virus and its mutants. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 25;87(1):31–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90558-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A., Bishop D. H. Primary in vivo transcription of vesicular stomatitis virus and temperature-sensitive mutants of five vesicular stomatitis virus complementation groups. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1238–1252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1238-1252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A., Lafay F. Etude des mutants thermosensibles du virus de la stomatite vésiculaire appartenant au groupe de complémentation I. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1973 Mar;124(2):261–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Manders E. K. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. IV. Transcription by standard virus in the presence of defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):909–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.909-916.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M., Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. RNA- temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus: L-protein thermosensitivity accounts for transcriptase restriction of group I mutants. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):596–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.596-603.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafay F. Envelope proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: effect of temperature-sensitive mutations in complementation groups III and V. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1220-1228.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Engelhardt D. L., Hunt J. M., Sekellick M. J. Interferon action: inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA synthesis induced by virion-bound polymerase. Science. 1971 Nov 5;174(4009):593–598. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4009.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. Conditional lethal mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:85–116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R., Duncan I. B., Stevenson M. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus, New Jersey serotype. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):836–841. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.836-841.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R., Wunner W. H. Genetic and physiological properties of temperature-sensitive mutants of Cocal virus. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):677–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.677-683.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Flamand A., Clark H. F., Obijeski J. F., Roy P., Bishop D. H. Detection of homologous RNA sequences among six rhabdovirus genomes. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):250–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.250-252.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider L. G., Dietzschold B., Dierks R. E., Matthaeus W., Enzmann P. J., Strohmaier K. Rabies group-specific ribonucleoprotein antigen and a test system for grouping and typing of rhabdoviruses. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):748–755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.748-755.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi J. F., Pringle C. R. Effect of temperature-sensitive mutations on the virion-associated RNA transcriptase of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Levine M. RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus and a small plaque mutant: effects of cycloheximide. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):253–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.253-264.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



