Figure 4. Two-sample t-test results for different features: p-values vs. FDR threshold.
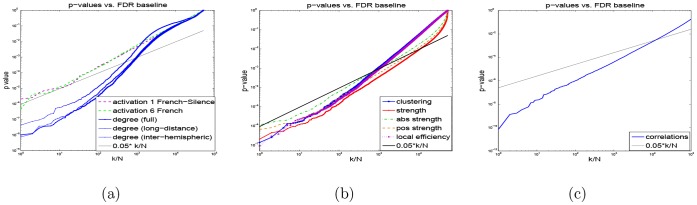
(a) Activations vs. normalized degrees; (b) clustering coefficients, strength, absolute strength, positive strength, and local efficiency of each voxel; (c) 200,000 randomly selected pairwise correlations. The null hypothesis for each feature assumes no difference between the schizophrenic vs normal groups. P-values of the features are sorted in ascending order and plotted vs FDR baseline; FDR test select voxels with 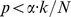 ,
,  - false-positive rate,
- false-positive rate, 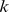 - the index of a p-value in the sorted sequence, N - the total number of voxels. Note that graph-based features yield a large number of highly-significant (very low) p-values, staying far below the FDR cut-off line, while only a few voxels survive FDR in case of (unnormalized) activation maps in panel (a): 7 and 2 voxels in activation maps 1 (contrast “FrenchNative – Silence”) and 6 (“FrenchNative”), respectively, while the rest of the activation maps do not survive the FDR correction at all.
- the index of a p-value in the sorted sequence, N - the total number of voxels. Note that graph-based features yield a large number of highly-significant (very low) p-values, staying far below the FDR cut-off line, while only a few voxels survive FDR in case of (unnormalized) activation maps in panel (a): 7 and 2 voxels in activation maps 1 (contrast “FrenchNative – Silence”) and 6 (“FrenchNative”), respectively, while the rest of the activation maps do not survive the FDR correction at all.
