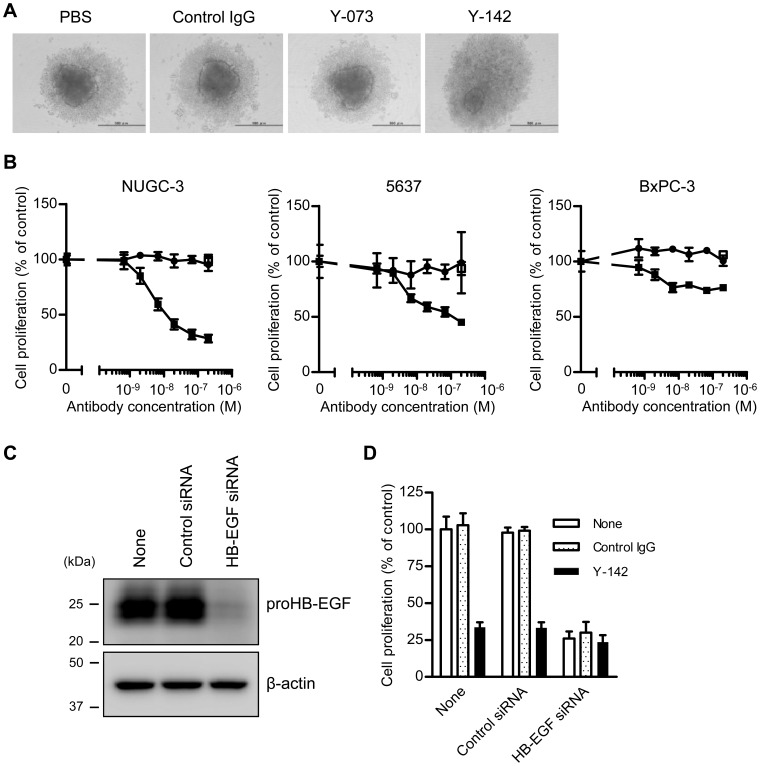
Figure 3. Spheroid-forming and cell-proliferation effects of proHB-EGF.
Spheroid formation and cell proliferation by proHB-EGF function were assessed under Y-142 treatment. The cells were seeded into a spheroid culture plate in the presence of 1% serum. After a 1-d incubation period, the cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of anti-HB-EGF antibody and cultured for 3 d. A. Spheroid formation of NUGC-3 cells. The bar in each image indicates 500 µm. B. Inhibition of proHB-EGF-dependent cell proliferation by Y-142. Cell proliferation was measured by CellTiter-Glo and is shown as the percentage of the proliferation of PBS-treated cells. Control IgG, white square; Y-142, black square; Y-073, black circle. The data points represent the mean ± SD of values acquired in triplicate. C. Reduction in HB-EGF protein by HB-EGF siRNA. Cell lysates of siRNA-transfected NUGC-3 cells were subjected to SDS-PAGE. HB-EGF was detected by western blotting, with β-actin as the internal control. D. Confirmation of proHB-EGF-dependent cell proliferation by HB-EGF siRNA. NUGC-3 cells were transfected with HB-EGF siRNA prior to spheroid culture. One day after the siRNA transfection, the cells were seeded into a spheroid culture plate. Cell proliferation was measured by CellTiter-Glo and shown as a percentage of the cell proliferation of PBS-treated cells. The data points represent the mean ± SD of values acquired in triplicate.