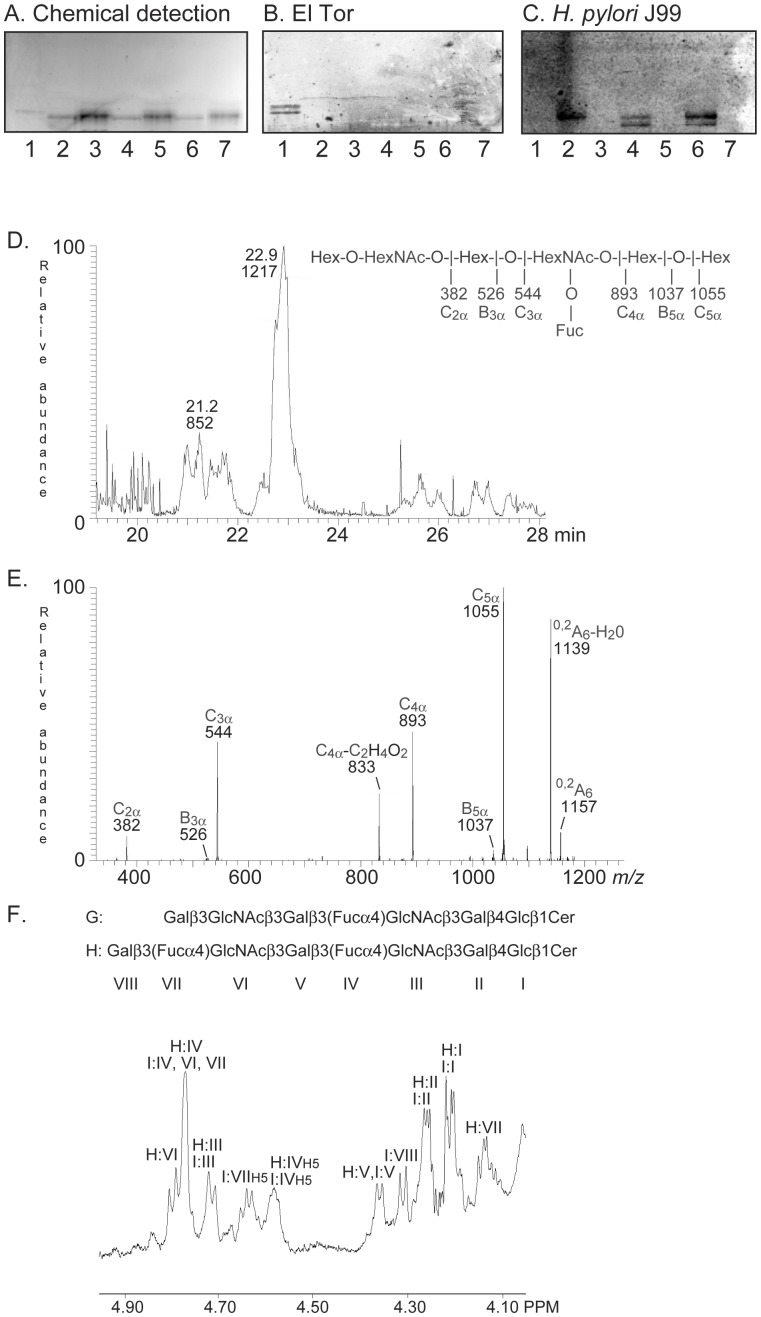
Figure 2. Characterization of the El Tor binding glycosphingolipid of human small intestine.
(A) Chemical detection by anisaldehyde. (B) Autoradiogram obtained by binding of V. cholerae strain JBK 70. (C) Autoradiogram obtained by binding of H. pylori strain J99. The lanes were: Lane 1, fraction HI-I from human small intestine, 4 µg; Lane 2, NeuAcα3Galβ4(Fucα3)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer (sialyl-Lex-octaosylceramide), 4 µg; Lane 3, Galβ4(Fucα3)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer (Lex-heptaosylceramide), 4 µg; Lane 4, NeuAcα3Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4(Fucα3)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer (VIM2), 4 µg; Lane 5, Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4(Fucα3)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer (de-sialo VIM2), 4 µg; Lane 6, NeuAcα3Galβ4(Fucα3)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4(Fucα3)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer (sialyl-dimeric-Lex), 4 µg; Lane 7, Galβ4(Fucα3)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4(Fucα3)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer (dimeric-Lex), 4 µg. The sialic acid binding H. pylori strain J99 (C) was used as a control for removal of sialic acid from the compounds in lanes 3, 5 and 7 [14]. (D) Base peak chromatogram from LC-ESI/MS of the oligosaccharides derived from fraction HI-I by hydrolysis with Rhodococcus endoglycoceramidase II. (E) MS2 spectrum of the [M-H+]− ion at m/z 1217 (retention time 22.9 min). (F) Anomeric region of the 600 MHz 1H NMR spectrum of fraction HI-I (30°C). The designations G and H refer to Table 1.