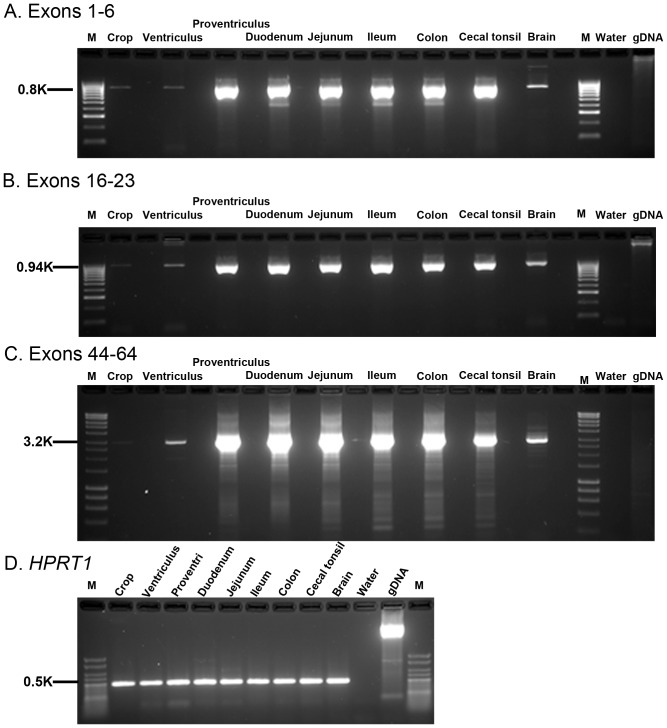
Figure 5. Expression of MUC2 in the gastrointestinal tract and brain.
RNAs were reverse transcribed using SMARTScribe™ (Clontech) with Oligo d(T) to generate long, full-length cDNA. We performed 33 cycles of RT-PCR amplification on 40 ng of cDNA with three sets of MUC2 primers. Alternating blank lanes lack reverse transcriptase. A. Exons 1–6. MUC2 is highly expressed in the proventriculus, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, colon, and cecal tonsil, with lower levels in the brain and minimal expression in the crop and ventriculus. Although these primers (P27 and P2) amplify genomic DNA, Genomic DNA controls demonstrate the lack of genomic contamination in all samples, indicating that observed expression is from cDNA B. Exons 16–23. MUC2 is highly expressed in the proventriculus, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, colon, and cecal tonsil, with lower levels in the brain and minimal expression in the crop and ventriculus. Although these primers (P7 and P8) amplify genomic DNA, Genomic DNA controls demonstrate the lack of genomic contamination in all samples, indicating that observed expression is from cDNA C Exons 44–65. A touchdown long-range PCR was used to amply the 3′ end of MUC2 using an internal primer and a primer targeting the exact end of the MUC2 cDNA (P30 and P29). This region demonstrates a very similar pattern of expression, with high levels detected in all tissues, except brain, which shows low-level expression,and ventriculus which has minimal expression. No expression is detected in the crop in this analysis. D. HPRT1 control gene. All samples express HPRT, and lack the presence of the genomic DNA band, indicating that the samples do not have genomic contamination. RT-PCR products were examined by electrophoresis through a 2.5% agarose gel in 0.5× TBE (A and B) or 1.2% TAE; water and genomic DNA were used as controls.