Fig. 1.
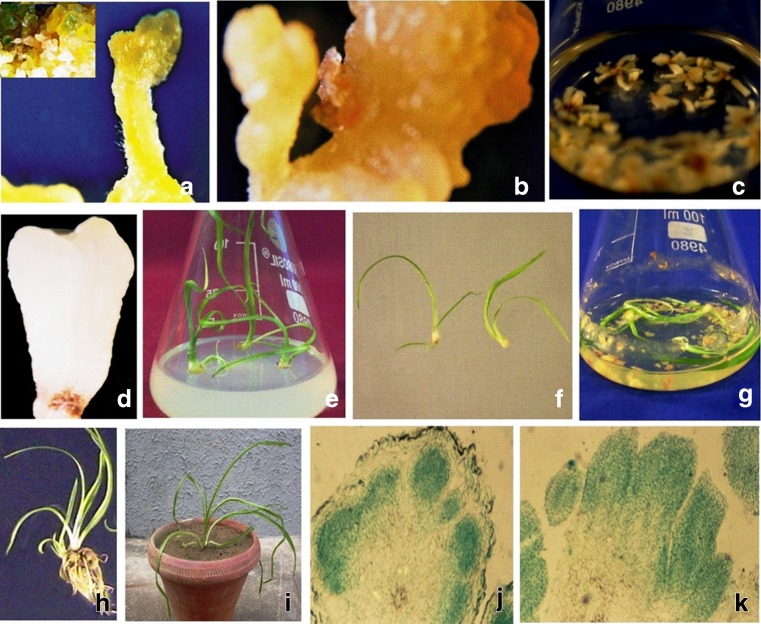
Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis in C. borivilianum. a. mature somatic embryo on solid embryogenic medium [MS medium containing 1.79 mM NH4NO3, 10.72 mM KNO3, 1.13 μM 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), 7.38 μM 2-isopentenyladenine (2-iP) and 0.76 mM proline] with 3 % sucrose after 4 weeks of culture (inset a. induction and development of somatic embryos on same medium); b. mature somatic embryo after 4 weeks of culture on solid embryogenic medium containing sucrose and PEG (polyethylene glycol), (3 % each); c. somatic embryos at different stages of maturation in liquid embryogenic medium after 4 weeks of culture; d. a mature somatic embryo in liquid medium; e. plantlets regenerated after 4 weeks of culture of mature somatic embryos on solid MS medium supplemented with 15.54 μM 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP), (somatic embryos matured on solid embryogenic medium containing 3 % sucrose); f. plantlets regenerated after 4 weeks of culture of mature somatic embryos on solid MS medium having 15.54 μM BAP, [somatic embryos matured on embryogenic medium containing sucrose and PEG (3 % each)]; g. plantlets regenerated after 4 weeks of culture of somatic embryos on liquid MS medium containing 15.54 μM BAP, (somatic embryos matured in liquid embryogenic medium); h. somatic embryo derived plantlet with developed root system after 6 weeks of culture; i. C. borivilianum plant regenerated through somatic embryogenesis in earthen pot after 11 weeks of hardening; j. globular somatic embryos appearing from surface of embryogenic cell mass in histological section; k. somatic embryos at advanced stage of maturation