Figure 4.
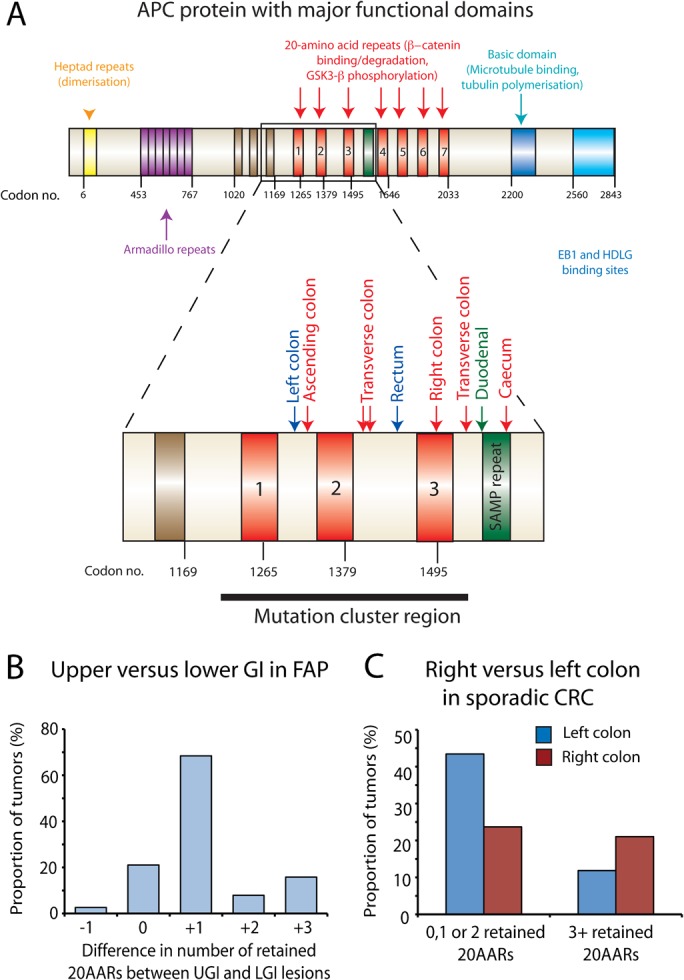
The adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) mutation spectrum varies with intestinal region in familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and sporadic gastrointestinal tumours. (A) Mutation spectra of upper and lower gastrointestinal (GI) lesions taken from the same FAP patient. The major functional domains of the APC protein are shown with an enlargement of the mutation cluster region. The number of retained 20-amino acid β-catenin binding repeats (20AARs) was calculated in upper GI (UGI) and lower GI (LGI) lesions taken from the same individual FAP patient(s) after determination of the mutation spectra of each lesion. The mutations for one individual patient (patient 1, online supplementary table 3) are mapped out (UGI lesion, green; right colon, red; left colon, blue) (B). UGI lesions in FAP retain significantly more 20AARs than LGI lesions taken from the same patient. The number of retained repeats from LGI lesions was subtracted from the number of repeats retained in the same patients' UGI lesions and the difference plotted. Significantly more repeats were retained in UGI lesions resulting in a more modest Wnt perturbation in these lesions (p<0.001, binomial test). (C) Right sided sporadic colorectal cancers and cell lines retain significantly more 20AARs than left sided lesions. Leisons in our sporadic data set of 76 tumours (online supplementary table 4A and B) were categorised by their distribution and the cumulative number of retained 20AARs after identification of first and second hits at APC in all lesions. Tumours retaining a cumulative total of three or more 20AARs were more likely to arise proximally whereas on the left side of the colon, mutations that retain fewer 20AARs were optimally selected to produce a greater Wnt perturbation in the resultant polyp (p=0.03, Fishers Exact test).
