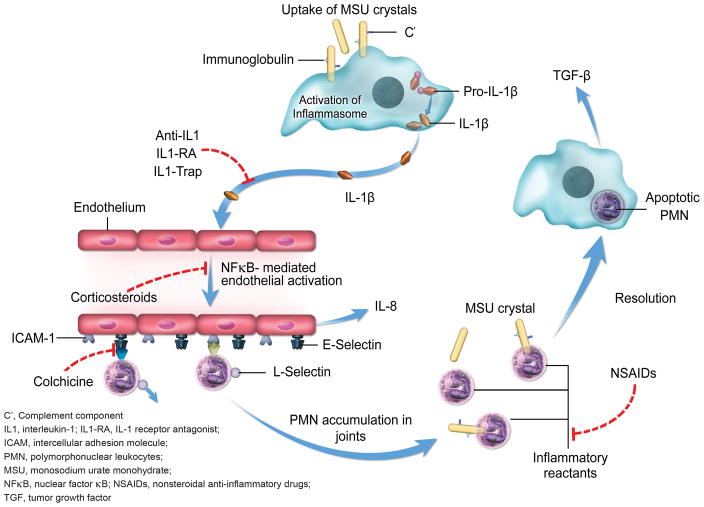
Figure 1. The most common mechanisms of therapeutic anti-inflammatory action of gouty arthritis drugs.
Colchicine, NSAIDs, and glucocorticoids act on many different molecular targets; the mechanisms displayed herein are the most likely targets for reduction of monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation when these drugs are administered at the recommended therapeutic doses. Anti-IL-1, IL1-RA, and IL1-Trap therapies act specifically to block IL-1β.