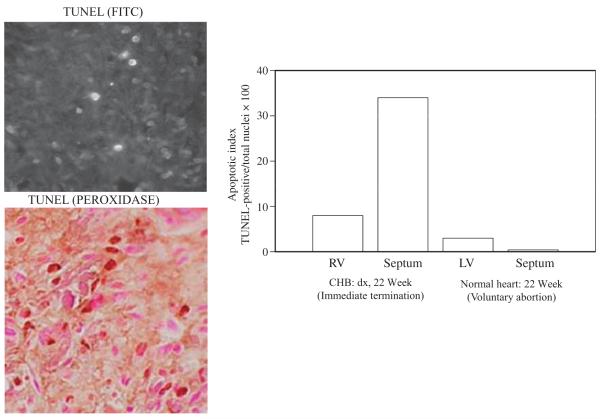
Fig. 1.
Histological evidence of increased apoptosis in conduction tissue from a foetus with congenital heart block (CHB). Shown are longitudinal sections through septum of a 22-week-old foetus with CHB. Apoptotic cells were identified by TUNEL fluorescein isothiocyanate staining (Left, upper) or TUNEL peroxidase (Left, lower). Apoptotic cells (brown nuclei) are interspersed with nonapoptotic cells (purple nuclei). For the 22 week foetus and a matched healthy heart, values (right) on the Y axis are the mean apoptotic index (AI), expressed as AI = (TUNEL-positive nuclei/total nuclei) × 100, where the total number of nuclei is the number of nonapoptotic nuclei plus the number of apoptotic (TUNEL-positive) nuclei. One hundred cells were counted in 3–5 fields for each cardiac section. RV, right ventricle; LV, left ventricle; CHB, congenital heart block. Reprinted from Rheum Dis Clin North Am, Vol. 30, Robert M. Clancy & Jill P. Buyon, More to death than dying: apoptosis in the pathogenesis of SSA/Ro-SSB/La-associated congenital heart block, pages 589–602, 2004, with permission from Elsevier.