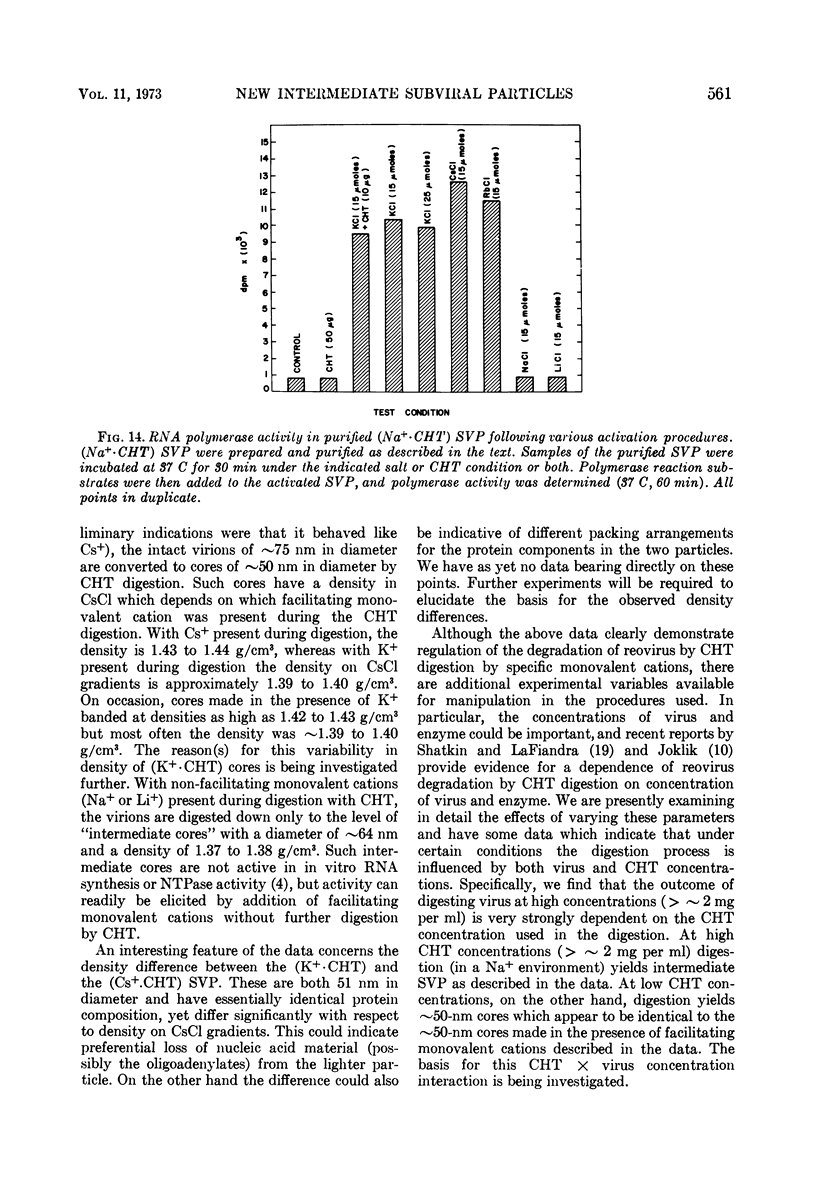
Abstract
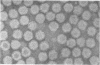
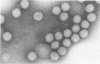
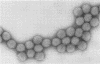
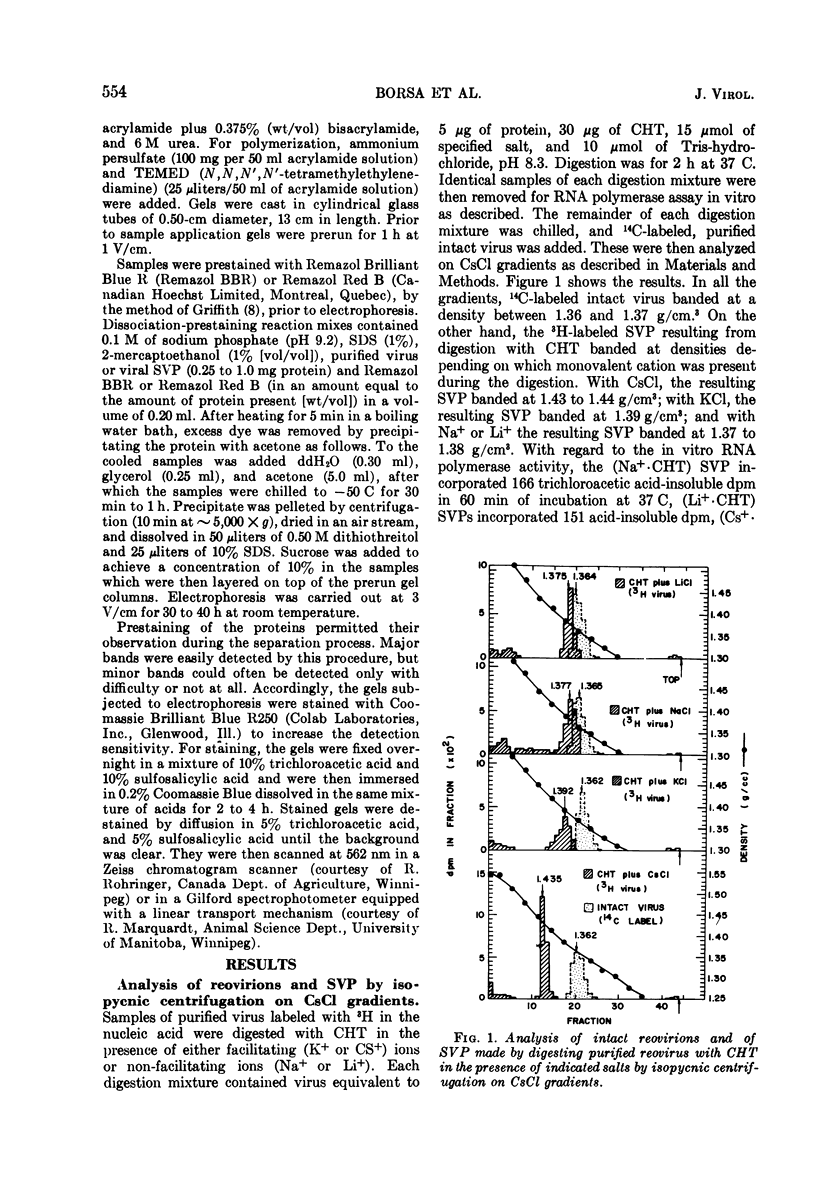
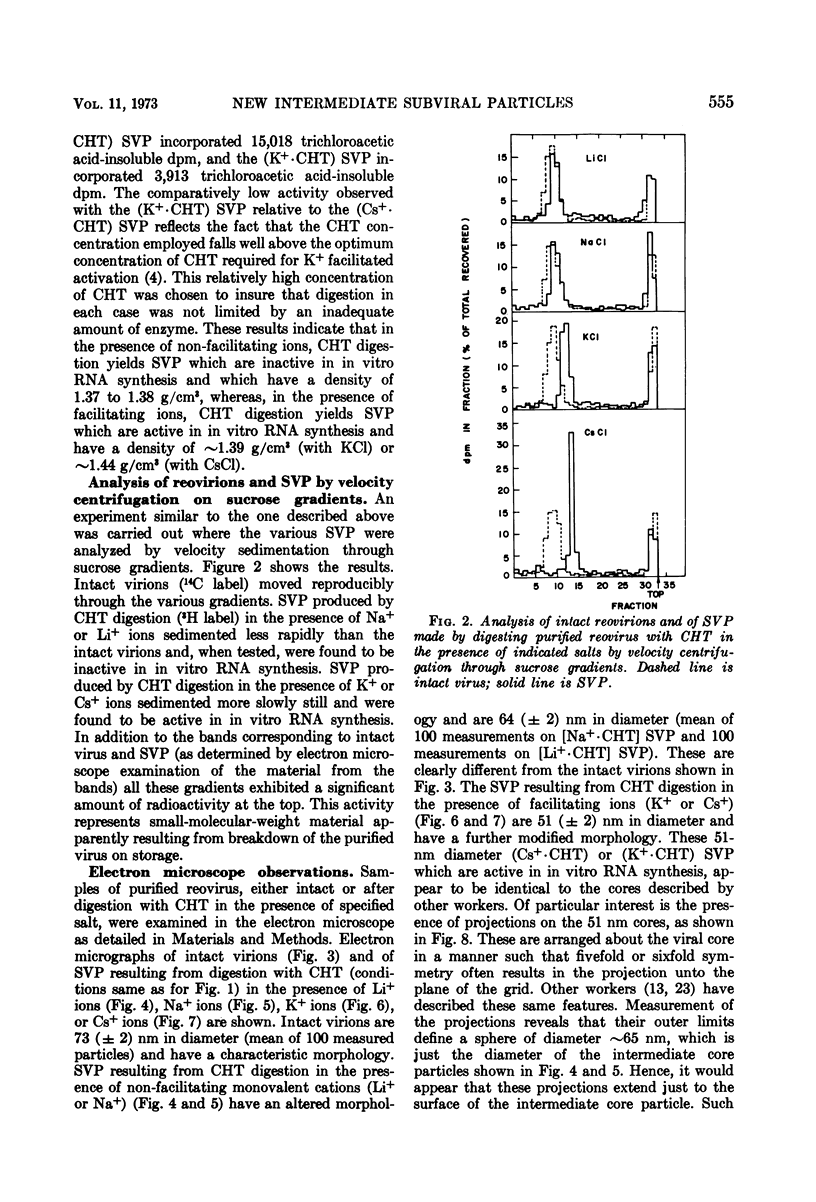
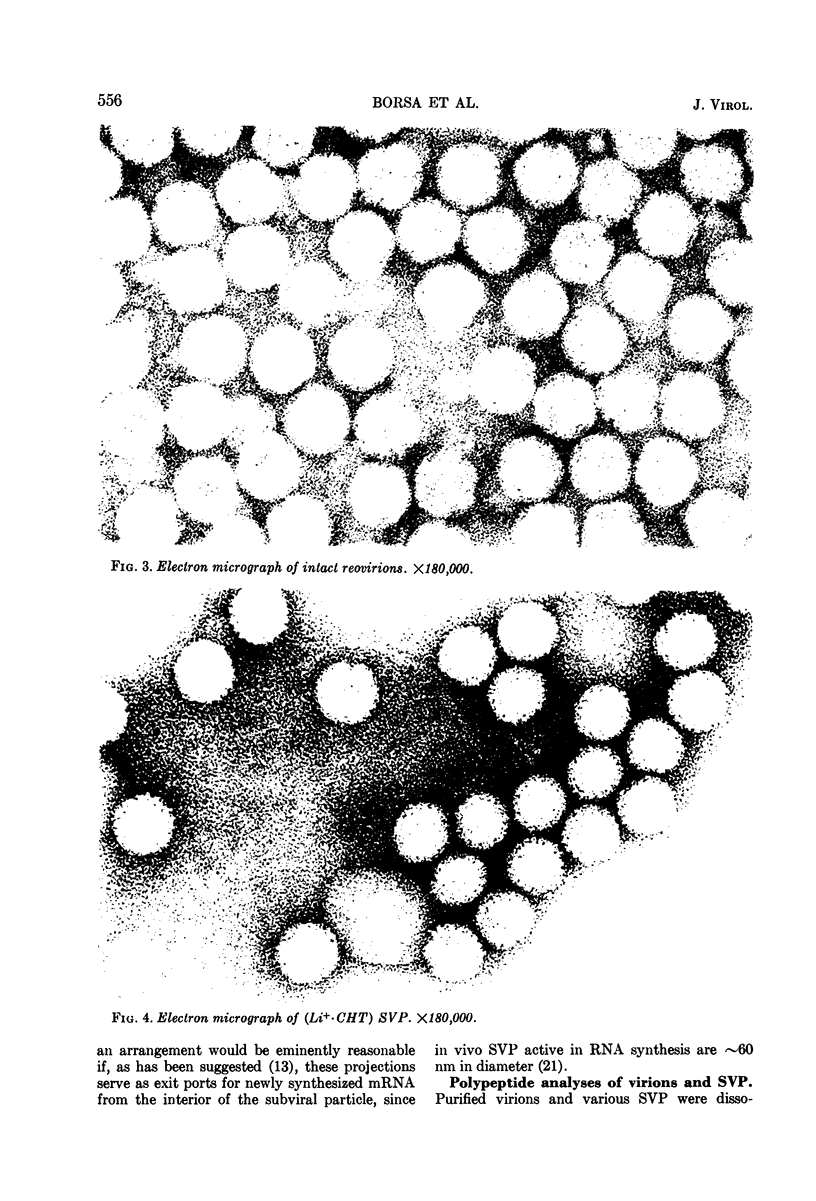
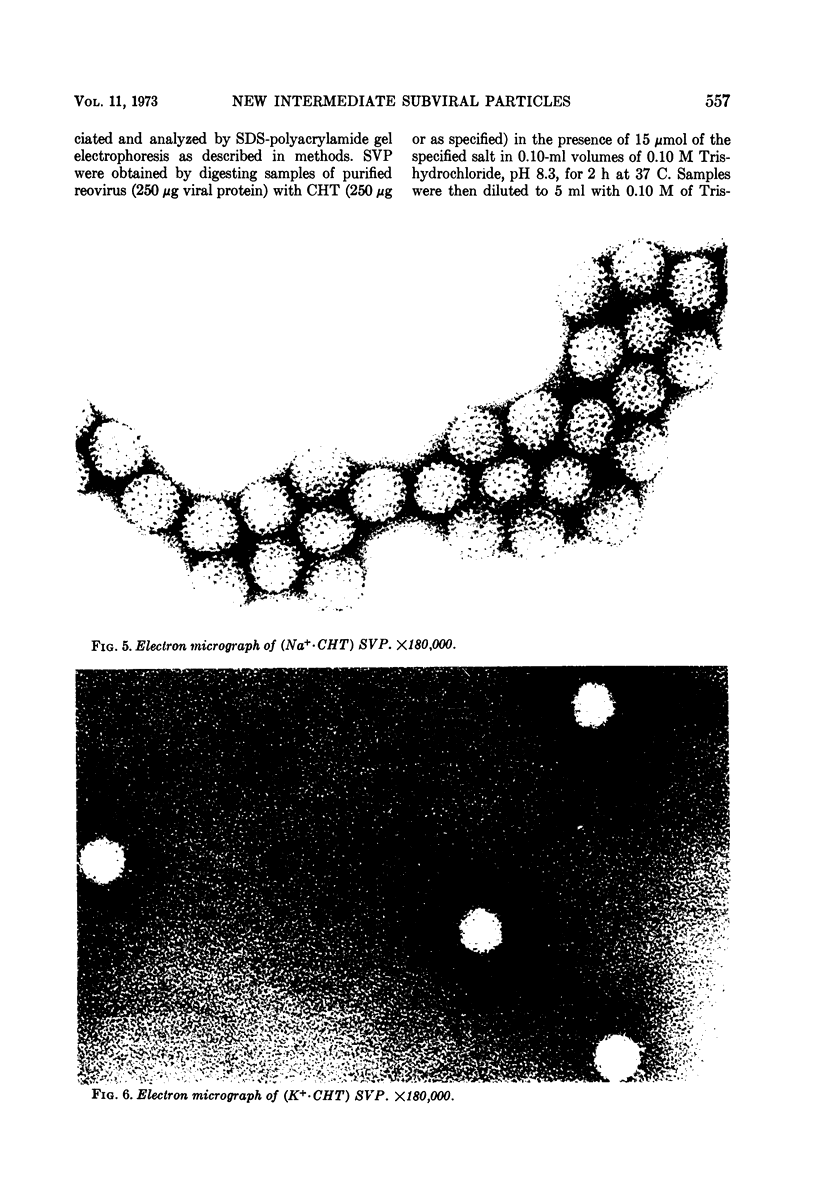
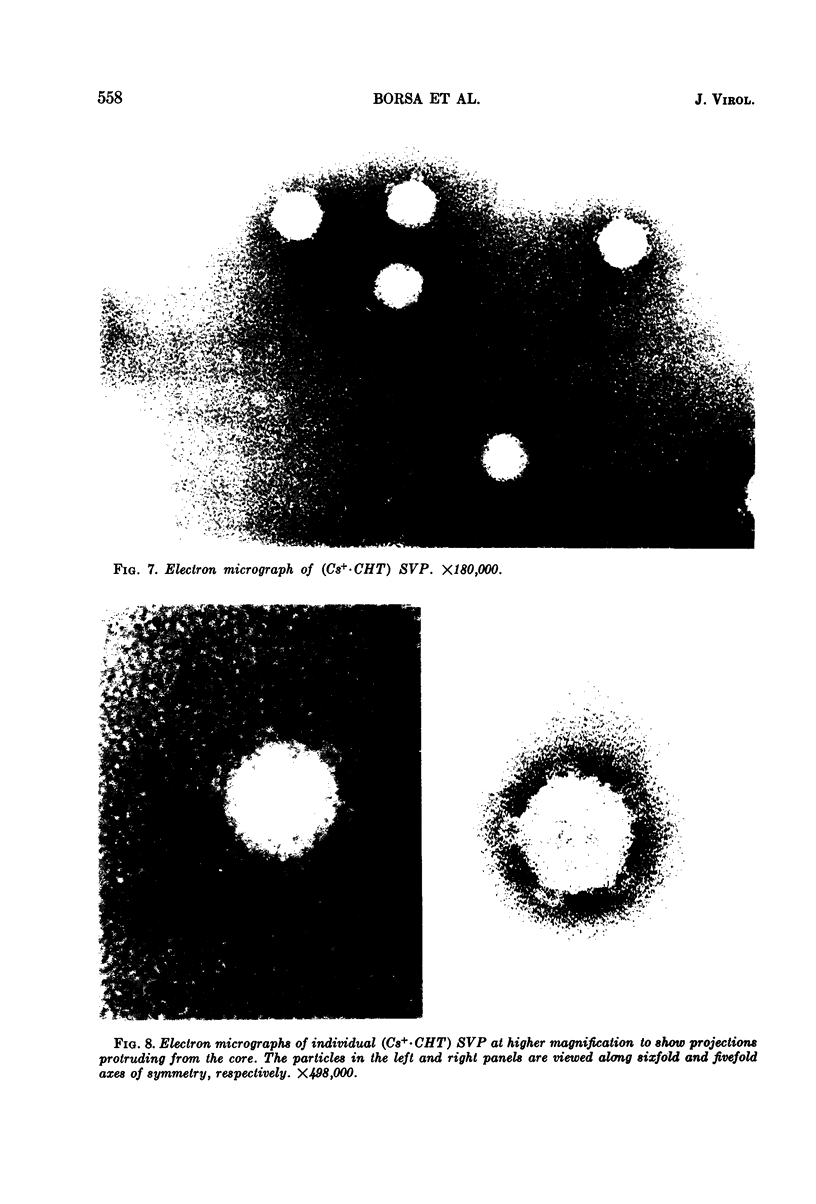
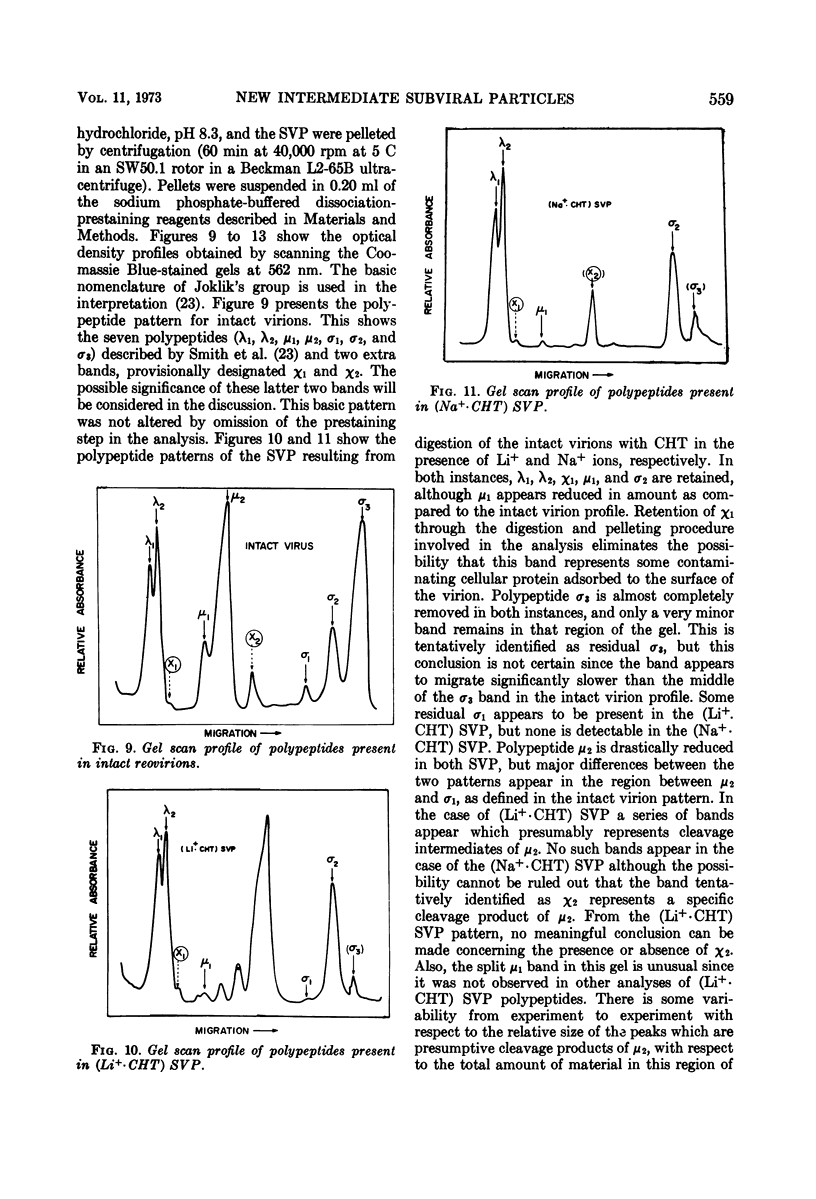
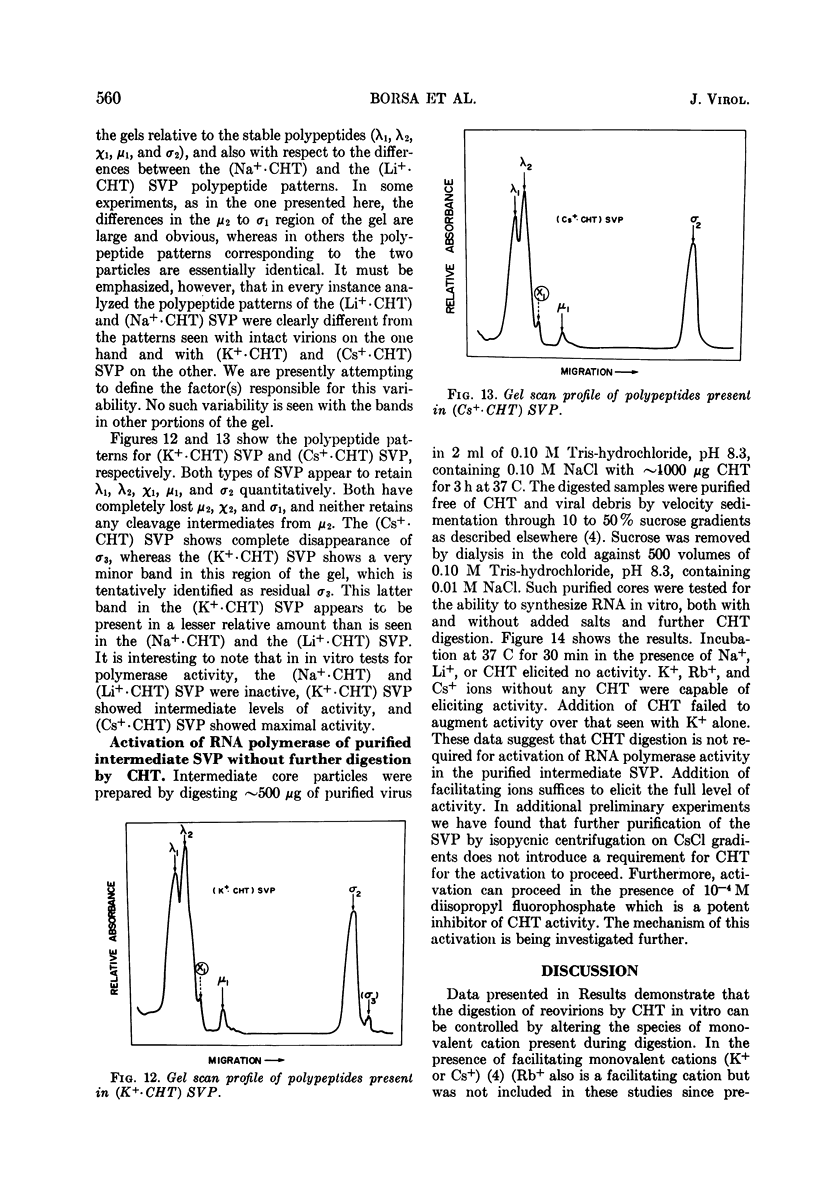
Reovirus virions, grown in suspension cultures of L cells and extensively purified by density gradient and velocity gradient centrifugation after their release from cell debris by fluorocarbon extraction, are characterized by a mean particle diameter of 73 nm and a density in CsCl of 1.36 to 1.37 g/cm3. Treatment of intact virions by chymotrypsin (CHT) digestion in vitro converts them to subviral particles (SVP) having characteristics which are determined by the species of monovalent cation present during the digestion. In the presence of Cs+ ions, CHT converts the virions to SVP of mean diameter 51 nm and density 1.43 to 1.44 g/cm3. In the presence of K+ ions, the conversion is to SVP of diameter 51 nm and density 1.39 to 1.40 g/cm3. The SVP made in the presence of either Cs+ or K+ possess an extremely active RNA polymerase and nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase (NTPase) activity in vitro and are resistant to further digestion by CHT. Treatment of intact virions with CHT in the presence of Na+ or Li+ ions results in their conversion to SVP of mean diameter 64 nm and density 1.37 to 1.38 g/cm3. Such SVP are not active in in vitro RNA synthesis or NTP hydrolysis and are resistant to further digestion by CHT even during prolonged exposure to high concentrations of enzyme. Addition of Cs+ or K+ ions to the digestion mixture allows conversion of the 64-nm diameter SVP to 51-nm diameter SVP in which the RNA polymerase and NTPase are active in vitro. Analysis of the proteins present in intact virions and in the different SVP reveals clear differences which indicate that the conversions are accomplished by removal or cleavage of particular species of polypeptides.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano Y., Katagiri S., Ishida N., Watanabe Y. Spontaneous degradation of reovirus capsid into subunits. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):805–808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.805-808.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C., Silverstein S. C., Levin D. H., Acs G. Regulation of the reovirus RNA transcriptase by a viral capsomere protein. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):648–654. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Graham A. F. Reovirus: RNA polymerase activity in purified virions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Sargent M. D., Long D. G., Chapman J. D. Extraordinary effects of specific monovalent cations on activation of reovirus transcriptase by chymotrypsin in vitro. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):207–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.207-217.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Zweerink H. J. Fate of parental reovirus in infected cell. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):544–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S., Bullivant S., Bellamy A. R. Viral RNA polymerases: electron microscopy of reovirus reaction cores. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):694–696. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J. Comparison of the virion polymerase of reovirus with the enzyme purified from reovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):610–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.610-620.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith I. P. Immediate visualization of proteins in dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels by prestaining with Remazol dyes. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):402–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reovirions. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuler A. M., Mendelsohn N., Klett H., Acs G. Four base-specific nucleoside 5'-triphosphatases in the subviral core of reovirus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1209–1213. doi: 10.1038/2251209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh P. C., Shatkin A. J. Structural proteins of reoviruses. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1353–1359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1353-1359.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luftig R. B., Kilham S. S., Hay A. J., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. An ultrastructural study of virions and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):170–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYOR H. D., JAMISON R. M., JORDAN L. E., VANMITCHELL M. REOVIRUSES. II. STRUCTURE AND COMPOSITION OF THE VIRION. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1548–1556. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1548-1556.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor H. D., Jordan L. E. Preparation and properties of the internal capsid components of reovirus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Sep;3(2):233–237. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K. An in vitro protein synthesizing system from mouse L fibroblasts infected with reovirus. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):724–733. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RHIM J. S., SMITH K. O., MELNICK J. L. Complete and coreless forms of reovirus (ECHO 10). Ratio of number of virus particles to infective units in the one-step growth cycle. Virology. 1961 Dec;15:428–435. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., LaFiandra A. J. Transcription by infectious subviral particles of reovirus. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):698–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.698-706.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Astell C., Levin D. H., Schonberg M., Acs G. The mechanisms of reovirus uncoating and gene activation in vivo. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Schonberg M., Levin D. H., Acs G. The reovirus replicative cycle: conservation of parental RNA and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):275–281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASQUEZ C., TOURNIER P. NEW INTERPRETATION OF THE REOVIRUS STRUCTURE. Virology. 1964 Sep;24:128–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASQUEZ C., TOURNIER P. The morphology of reovirus. Virology. 1962 Aug;17:503–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K. Essential and nonessential noncapsid reovirus proteins. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):716–723. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]