Figure 2.
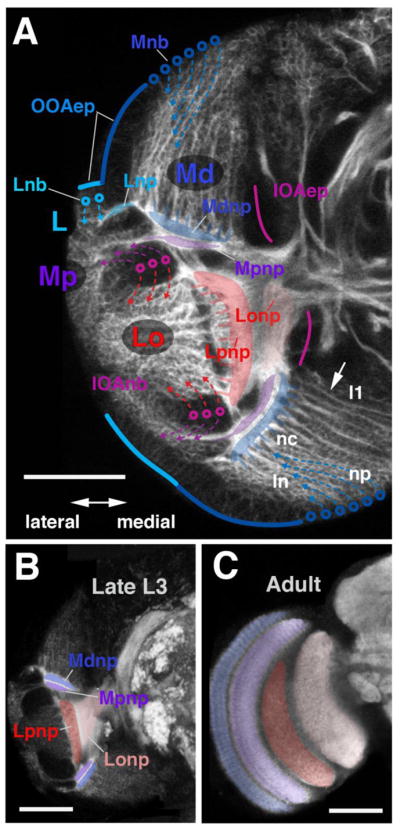
Fatemap of the late larval optic lobe. (A) Confocal cross-section of late larval optic lobe of left brain hemisphere, labelled with anti-Neurotactin (white). Epithelial inner and outer optic anlagen (IOAep; magenta line; OOAep, blue line) are only faintly positive for anti-Neurotactin and appear dark. Neuroblasts arising from the outer optic anlage (Lnb, cyan circles; Mnb, blue circles) and inner optic anlage (IOAnb, magenta circles) are moderately strongly labelled; neurons and outgrowing axons are strongly labelled. Arrows on hatched lines indicate direction in which neurons are given off by their respective neuroblasts. Neurons of the distal medulla (Md) form discrete lineages, each one emitting a bundle of axons towards centrally (arrow). Tips of these axons gather in a plexus that forms the forerunner of the distal medulla neuropile (Mdnp, shaded blue). Lineages located medially belong to neuroblasts formed from the OOAm first (l1); the further lateral a lineage is located (ln), the later the corresponding neuroblast was formed. In each given lineage, neurons born early are located centrally, far from the surface (nc); late born neurons are peripherally (np). Neuroblasts of the IOA give off neurons outwardly (purple arrows) and inwardly (red arrows). The former makes up the proximal medulla (Mp) and the latter makes up the lobula and lobula plate (Lo; see also digital models in panel E). Axons of both of these neuron populations grow medially and form the proximal medulla neuropile (Mpnp, shaded in purple), the lobula plate neuropile (Lpnp, red) and the lobula neuropile (Lonp, pink). (B, C) Confocal cross-sections of late larval brain (B) and adult brain (C), labelled with anti-DNcadherin to visualize optic neuropiles (white). Left hemisphere, lateral to the left, dorsal up. Optic lobe neuropiles of the larva and adult are rendered in corresponding colors; abbreviations and color code as in A. Bars: 40μm
