Figure 6.
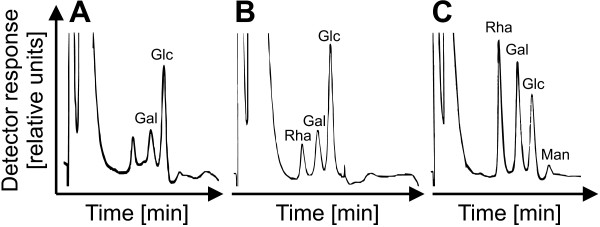
Effect of the co-incubation of X. campestris pv. campestris with plant cell wall material on the composition of the dissolved monosaccharides. The identity and relative amounts of the monosaccharides in the supernatant of X. campestris pv. campestris co-incubated with cell wall material of C. annuum was determined by HPAEC. The sugars were separated and identified using an isocratic elution with10 mM sodium hydroxide and amperometric detection on a CarboPac® PA-100 column, a set up that allows detecting the dissolved neutral sugars. The results were compared to the supernatant of an X. campestris pv. campestris culture that had had no contact to plant cell wall material, and to analogously treated cell wall material that had not been incubated with bacteria. The supernatants of plant cell wall material (A) and the X. campestris pv. campestris culture (B), which were analyzed as controls, were both mainly composed of glucose (Glc), galactose (Gal), and rhamnose (Rha). When plant cell wall material and X. campestris pv. campestris culture were co-incubated (C), the amounts of rhamnose and galactose increased dramatically, reverting the original relative abundances. In addition, small amounts of mannose (Man) became detectable.
