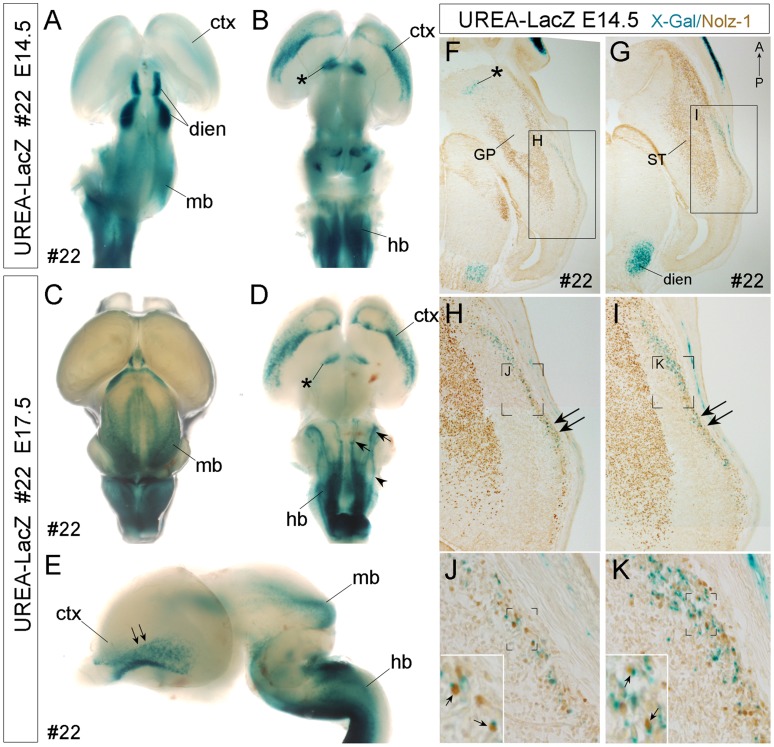
Figure 5. Detection of X-gal-positive signals in specific brain regions and LacZ+/Nolz-1+ cells in the ventral cortex of line #22 UERA-LacZ embryos.
A–E: Whole mount X-gal staining of E14.5 (A, B) and E17.5 (C–E) embryonic brains. X-gal-positive signals are detected in the cerebral cortex (ctx, B, D), ventral forebrain (asterisk, B, D), diencephalon (dien, A), midbrain (mb, A, C, E) and hindbrain (hb, B, D, E) regions. D: Three X-gal-positive longitudinal columns (arrowhead, arrows) are found in the hindbrain. The arrows indicate the X-gal-positive columns which are also observed in the hindbrain of line #26 (Fig. S6), whereas the arrowhead indicates an additional X-gal-positive column found only in line #22. E: The double arrows indicate the ventral-to-dorsal gradient of X-gal-positive signals in the ventral cortex. A, C: dorsal view; B, D: ventral view; E: lateral view. F–K: Double labeling of X-gal-positive signal and Nolz-1 protein on E14.5 horizontal forebrain sections of line#22 UREA-LacZ embryos. Nolz-1 is expressed in the striatum (ST), but not in the globus pallidus (GP), nor in the X-gal-positive domains in ventral forebrain (asterisk, F) and diencephalon (dien, G). In the lateral cortex, a stream of X-gal-positive cells is observed. Within this cell stream, many X-gal-positive cortical cells co-expressing Nolz-1 (small arrows in insets of J, K) are detected. Anterior is to the top of figures F–K. Figure F is at ventral level and Figure G is at more dorsal level. The boxed regions in F, G and the bracketed regions in H, I, J, K are shown at high magnification in H, I, J, K, and insets in J, K, respectively. IV, fourth ventricle; mb, midbrain.